Home > News > CD14 Antibodies: Deciphering Dual Regulatory Mechanisms in Inflammasome Activation and Lipid Delivery
CD14 Antibodies: Deciphering Dual Regulatory Mechanisms in Inflammasome Activation and Lipid Delivery
- 1. Concept
CD14, a glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored protein, is a central mediator of the innate immune system with multifaceted functions. Traditionally recognized for recognizing bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and delivering it to the Toll-like receptor 4/MD-2 complex (aided by LPS-binding protein), CD14’s role extends to recognizing endogenous damage-associated molecular patterns—particularly oxidized phospholipids. This dual ligand recognition capability positions CD14 as a critical molecular bridge linking microbial infection and tissue damage responses, governing both immune surveillance and inflammation regulation. CD14 antibodies, developed by ANT BIO PTE. LTD., enable precise detection and functional analysis of this molecule, supporting research into its dual mechanisms of inflammasome activation and lipid delivery.
2. Research Frontiers
Cutting-edge research has uncovered CD14’s complex dual regulatory roles, driving innovations in immunology and inflammatory biology:
Dual Ligand Recognition: CD14 binds both exogenous LPS (pathogen-associated molecular patterns) and endogenous oxidized phospholipids (damage-associated molecular patterns), mediating distinct yet interconnected immune responses.
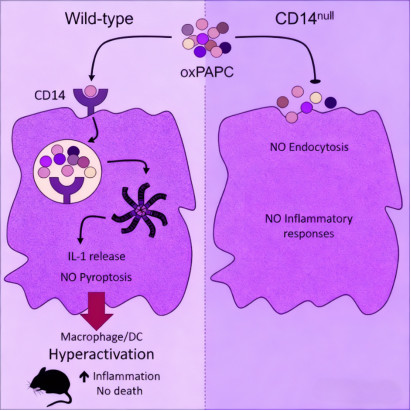
Oxidized Phospholipid Internalization: CD14 initiates ligand internalization via a TLR4-independent mechanism. Binding oxidized phospholipids triggers conformational changes, activating phospholipase Cγ and Syk kinase pathways to promote endocytosis of the CD14-ligand complex—leading to transient plasma membrane CD14 depletion and subsequent immunoregulation.
Dendritic Cell Hyperactivation: Under oxidized phospholipid stimulation, CD14 induces dendritic cells into a hyperactivated state, characterized by sustained interleukin-1 secretion and enhanced immunostimulatory capacity (without significant cell death). This depends on CD14-mediated delivery of oxidized phospholipids to intracellular compartments, activating the caspase-11-dependent inflammasome pathway.
Structural Basis of Ligand Binding: CD14’s N-terminal four hydrophobic regions form a conserved ligand-binding pocket, accommodating both oxidized phospholipids and LPS. Mutations in critical amino acid residues abolish binding to both ligands, explaining their competitive interaction and CD14’s multi-ligand recognition capability.
3. Research Significance
CD14 research holds profound implications for understanding innate immunity, inflammation regulation, and therapeutic development:
Mechanistic Innovation: It reveals novel links between lipid recognition, cellular endocytosis, and inflammasome activation, expanding knowledge of how the innate immune system integrates pathogen and tissue damage signals.
Cell-Type Specificity Insights: CD14 functions diverge across immune cells—inducing inflammasome activation in dendritic cells but distinct responses in macrophages—offering clues to the cellular specificity of immune reactions.
Therapeutic Potential: Targeting CD14 provides avenues for treating inflammatory diseases. In sepsis, modulating CD14 activity can balance immune defense and excessive inflammation; in chronic inflammation, blocking CD14-mediated endogenous danger signal recognition may alleviate pathology.
Research Tool Value: High-quality CD14 antibodies enable precise identification of monocytes/macrophages and analysis of their activation states, advancing studies in infection, autoimmunity, and tumor immunology.
4. Related Mechanisms, Research Methods, and Product Applications
Related Mechanisms
CD14 exerts dual regulatory effects through ligand-specific and cell-type-dependent mechanisms:
Lipid Delivery: Binds oxidized phospholipids or LPS via its N-terminal binding pocket, mediating internalization through phospholipase Cγ/Syk kinase signaling (oxidized phospholipids) or TLR4/MD-2 complex activation (LPS).
Inflammasome Activation: In dendritic cells, oxidized phospholipid internalization via CD14 activates caspase-11-dependent inflammasomes, driving IL-1 secretion and hyperactivation—distinct from classical inflammatory pathways.
Immunoregulatory Feedback: Transient CD14 depletion from the plasma membrane post-ligand internalization modulates subsequent LPS responses, forming a negative feedback loop to prevent excessive inflammation.
Research Methods
CD14 antibodies support core research techniques in immunology and inflammatory biology:
Expression and Localization Analysis: Immunohistochemistry (IHC) and flow cytometry to detect CD14 expression on monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells, with precise membrane localization.
Ligand Binding and Internalization Assays: Co-immunoprecipitation and confocal microscopy to study CD14-ligand interactions and endocytosis processes.
Inflammasome Activation Studies: Western blot and ELISA to measure caspase activation and IL-1 secretion, evaluating CD14-mediated hyperactivation of dendritic cells.
Functional Assays: LPS/oxidized phospholipid stimulation experiments to analyze CD14’s role in immune cell activation and inflammatory responses.
Product Applications by ANT BIO PTE. LTD.
ANT BIO PTE. LTD., via its sub-brand STARTER (specializing in high-performance antibodies), offers a curated portfolio of CD14 antibodies with exceptional specificity, sensitivity, and batch consistency. These products are rigorously validated for IHC, flow cytometry, and functional assays, enabling diverse research applications:
Monocyte/Macrophage Identification: Precise detection and distribution analysis of monocytes and macrophages in tissue microenvironments.
Inflammation and Immune Response Research: Evaluation of monocyte/macrophage infiltration and activation in infections, trauma, and autoimmune diseases.
Tumor-Associated Macrophage Studies: Identification and functional analysis of myeloid immune cells in the tumor microenvironment.
Innate Immunity Mechanism Exploration: Investigation of CD14’s role in LPS recognition, TLR4 signaling activation, and oxidized phospholipid-mediated inflammasome regulation.
5. Brand Mission
At ANT BIO PTE. LTD., our mission is to empower global innovative pharmaceutical companies, research institutions, and life science researchers with high-quality, high-value biological reagents and comprehensive solutions. Leveraging state-of-the-art technology platforms—including recombinant rabbit monoclonal antibody, recombinant mouse monoclonal antibody, rapid mouse monoclonal antibody, and recombinant protein development systems (E.coli, CHO, HEK293, Insect Cells), as well as the One-Step ELISA Platform and PTM Pan-Modification Antibody Platform—we strive to accelerate scientific discovery and translational research. Our sub-brands (Absin for general reagents and kits, STARTER for antibodies, and UA for recombinant proteins) synergize to address diverse research needs, contributing to breakthroughs in immunology, inflammatory disease research, and tumor biology. With certifications including EU 98/79/EC, ISO9001, and ISO13485, we uphold the highest standards of quality and reliability to support our mission of advancing human health through science.
6. Related Product List
| S0B5476 | Pacific Blue Mouse Anti-Human CD14 Antibody (S-631-50) | Host : Mouse Conjugation : Pacific Blue |
| S0B5943 | PerCP-Cy5.5 Rabbit Anti-Human CD14 Antibody (S-395-8) | Host : Rabbit Conjugation : PerCP-Cy5.5 |
| S0B8255 | Alexa Fluor® 647 Rat Anti-Mouse CD14 Antibody (S-R609) | Host : Rat Conjugation : Alexa Fluor® 647 |
| S0B8277 | Pacific Blue Rat Anti-Mouse CD14 Antibody (S-R609) | Host : Rat Conjugation : Pacific Blue |
| S0B8228 | PE-Cy7 Mouse Anti-Human CD14 Antibody (S-3449) | Conjugation : PE-Cy7 |
| S0B8197 | APC-Cy7 Mouse Anti-Human CD14 Antibody (S-3449) | Conjugation : APC-Cy7 |
7. AI Disclaimer
This article is AI-compiled and interpreted based on the original work. All intellectual property (e.g., images, data) of the original publication shall belong to the journal and the research team. For any infringement, please contact us promptly and we will take immediate action.
ANT BIO PTE. LTD. – Empowering Scientific Breakthroughs
At ANTBIO, we are committed to advancing life science research through high-quality, reliable reagents and comprehensive solutions. Our specialized sub-brands (Absin, Starter, UA) cover a full spectrum of research needs, from general reagents and kits to antibodies and recombinant proteins. With a focus on innovation, quality, and customer-centricity, we strive to be your trusted partner in unlocking scientific mysteries and driving medical progress. Explore our product portfolio today and elevate your research to new heights.
Related News
- Putting the Pressure On: Proven Flow Measurement Where Failure is Not an Option 3/12/2026
- Mouse T Cell Activation: A Systematic Guide to Developmental Differentiation and 3/12/2026
- Mouse T Cell Activation Kits: Enabling Efficient Immune Activation Through the C 3/11/2026
- Junshi Biosciences Announces NMPA Acceptance of New Drug Applications for Toripa 3/10/2026
- Rapport Therapeutics and Tenacia Biotechnology Announce Strategic Collaboration 3/10/2026
- Cas9 Antibodies: Ensuring Precision and Reproducibility in Gene Editing Research 3/10/2026
- Recombinant Rabbit Monoclonal Antibodies: Revolutionizing the Precision and Reli 3/9/2026
- Neural Research Antibodies: The Key to Unraveling the Mysteries of the Brain 3/8/2026
- The Key Role of CK-Pan Antibody in Cell Biology Research 3/7/2026
- Site-Selective Acetylation: Unlocking New Functional Horizons for Antibody Drugs 3/6/2026


