Home > News > How Do IGJ Antibodies Unravel the Mysteries of Immunoglobulin Structure and Function?
How Do IGJ Antibodies Unravel the Mysteries of Immunoglobulin Structure and Function?
- Immunoglobulins (Igs), the core effector molecules of humoral immunity, are glycoproteins secreted by plasma cells, which are B cells that have matured upon antigen stimulation.
Immunity/InflammationIGJ antibodyImmunoglobulinHumoral immunity
Recent Advances
I. What is the Basic Molecular Structure of Immunoglobulins?
Immunoglobulins (Igs), the core effector molecules of humoral immunity, are glycoproteins secreted by plasma cells, which are B cells that have matured upon antigen stimulation. Their basic structure exhibits a highly symmetrical "Y"-shaped conformation, formed by two identical heavy chains and two identical light chains linked by disulfide bonds. Based on differences in the amino acid sequences of their constant regions, heavy chains are classified into five types (μ, δ, γ, α, ε), corresponding to the five immunoglobulin classes: IgM, IgD, IgG, IgA, and IgE. Light chains are divided into two types, kappa (κ) and lambda (λ), based on structural differences in their constant regions.
Spatially, each polypeptide chain folds into multiple globular domains. A light chain contains one variable region domain and one constant region domain, while a heavy chain contains one variable region domain and three or four constant region domains. These domains play indispensable roles in maintaining the spatial conformation and biological functions of immunoglobulins. Particularly noteworthy is the hinge region between the CH1 and CH2 domains of the heavy chain, which is rich in proline residues, conferring significant flexibility to the molecule, allowing it to bind antigenic epitopes at different spatial locations simultaneously.
II. How Does the Immunoglobulin Variable Region Mediate Antigen Recognition?
The variable region, located at the N-terminus of the immunoglobulin polypeptide chains, forms the antigen-binding site through the combined contribution of the heavy chain variable region (VH) and light chain variable region (VL). In-depth research has revealed that each variable region contains three hypervariable regions known as Complementarity-Determining Regions (CDRs). These regions form a specific three-dimensional conformation in space, directly responsible for recognizing and binding antigenic epitopes. The antigen-binding site, composed collectively of the six CDRs (three from VH, three from VL), exhibits high specificity, enabling precise recognition and binding to corresponding antigenic epitopes.
The sequences outside the CDRs are relatively conserved, forming the Framework Regions (FRs). Their primary function is to maintain the overall structural scaffold of the variable region, providing stable spatial support for the CDRs. This structural design, combining variable and conserved elements, allows immunoglobulins to achieve specific recognition of a vast array of antigens while maintaining structural stability. It is worth emphasizing that each B cell clone produces immunoglobulins with unique variable region sequences; this diversity is the molecular basis for the specificity of the adaptive immune response.
III. What Effector Functions are Mediated by the Immunoglobulin Constant Region?
The constant region is located at the C-terminus of the immunoglobulin polypeptide chains, and its amino acid sequence is relatively conserved within the same immunoglobulin class and species. This region is crucial for the interaction of immunoglobulins with various immune molecules and cells in the body. Through their constant regions, immunoglobulins can activate the classical pathway of the complement system, with IgG and IgM exhibiting particularly strong complement-activating capabilities.
Additionally, the constant region mediates effector functions through interaction with Fc receptors (FcRs) expressed on the surface of various immune cells (e.g., macrophages, neutrophils, NK cells). This interaction can trigger processes such as phagocytosis (opsonization), Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity (ADCC), and degranulation. The constant region is also responsible for determining the tissue distribution and half-life of different immunoglobulin classes. For instance, the Fc region of IgG binds to the neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn), contributing to its long serum half-life.
IV. What Role Does the J Chain Play in Polymeric Immunoglobulins?
The J chain is a cysteine-rich polypeptide synthesized by plasma cells and plays a key role during immunoglobulin assembly. Its primary function is to link immunoglobulin monomers via disulfide bonds, facilitating the formation of polymers. In secretory IgA (sIgA), the J chain connects two IgA monomers to form a dimer. In IgM, the J chain participates in the assembly of five monomers into a pentameric structure.
Notably, J chain expression is closely associated with the production of polymeric immunoglobulins. Studies show that J chain deficiency impairs the assembly of polymeric IgA and IgM, thereby affecting mucosal immunity and early immune responses. Therefore, antibodies targeting the J chain hold significant value in studying the biological characteristics and functional mechanisms of polymeric immunoglobulins. Such antibodies can be used not only to detect J chain expression and distribution but also to help analyze the assembly process of polymeric immunoglobulins and their role in immune responses.
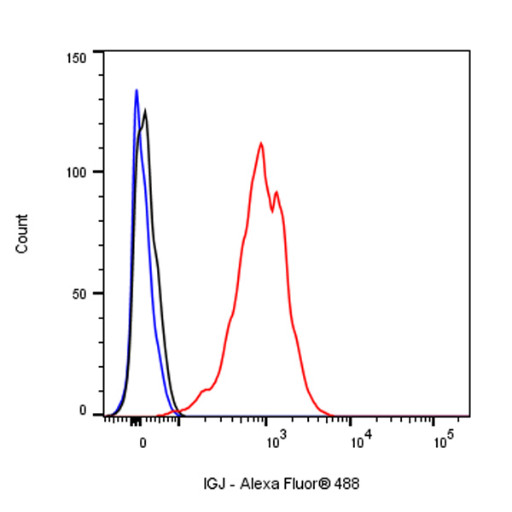
V. What Unique Biological Characteristics Do the Different Immunoglobulin Classes Possess?
IgG is the most abundant immunoglobulin in serum, accounting for approximately 75%-80% of total serum immunoglobulins. Its four subclasses differ in their ability to activate complement, cross the placenta, and their half-lives. IgG is the only immunoglobulin that can cross the placenta, providing crucial passive immune protection to newborns.
IgM exists as a pentamer and is the first antibody produced during the primary immune response. Its multivalent structure gives it significant advantages in antigen binding and complement activation.
IgA plays a key role in mucosal immunity. Secretory IgA (sIgA), by binding to the secretory component (SC), gains resistance to proteolytic degradation, allowing it to persist stably on mucosal surfaces.
IgE is primarily involved in allergic reactions and anti-parasitic immunity through binding to its high-affinity receptor (FcεRI).
IgD's function is not fully understood but it is considered an important component of the B cell receptor (BCR), particularly on naive B cells.
VI. How Have Artificially Prepared Antibody Technologies Developed?
With advances in molecular biology, genetic engineering antibody technologies have emerged. Researchers use gene recombination techniques to modify antibody genes, developing various novel antibody formats such as humanized antibodies, single-chain variable fragments (scFvs), and bispecific antibodies. These technological progressions have not only driven deeper basic research but also provided new tools and methods for disease diagnosis and treatment. It is particularly noteworthy that antibodies targeting auxiliary components of immunoglobulins, like the J chain (IGJ), demonstrate unique value in studying the structure and function of polymeric immunoglobulins.
VII. Which Manufacturers Provide IGJ Antibodies?
Hangzhou Start Bio-tech Co., Ltd.'s self-developed "IGJ Recombinant Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody" is a high-performance antibody product characterized by high specificity, excellent sensitivity, and exceptional staining consistency. This product is ideal for applications in plasma cell identification, immune response research, and related disease diagnosis.
Product Core Advantages:
High Specificity & Clear Localization: Precisely recognizes the Immunoglobulin J Chain (IGJ), demonstrating excellent plasma cell cytoplasmic staining specificity in FFPE samples, with a clear background and distinct signals, providing a reliable basis for accurate interpretation.
Excellent Staining Stability & Batch Consistency: Under strict quality control standards, the product exhibits excellent staining stability and minimal batch-to-batch variation, ensuring reliable and reproducible results under different experimental conditions, providing stable support for clinical diagnosis and basic research.
Suitable Key Application Scenarios:
This product is an ideal tool for conducting the following research:
Plasma Cell Identification & Differentiation Research: Serves as a specific marker for the precise identification and quantitative analysis of plasma cells in mucosal immunity, lymphoid tissues, and bone marrow.
Immunoglobulin Class Switch Research: Used to study the assembly and secretion processes of polymeric immunoglobulins like IgA and IgM.
Plasma Cell Disease Diagnosis: Aids in the diagnosis and differential diagnosis of plasma cell dyscrasias such as Multiple Myeloma and Waldenström's Macroglobulinemia.
Mucosal Immunity & Inflammation Research: For assessing the infiltration and functional status of plasma cells at mucosal sites in chronic inflammation and autoimmune diseases.
Professional Technical Support: We provide detailed product technical documentation, including complete IHC experimental protocols, optimized antigen retrieval methods, and clear interpretation criteria, fully committed to assisting customers in obtaining accurate and reliable results in immunological research and pathological diagnosis.
Hangzhou Start Bio-tech Co., Ltd. is always dedicated to providing high-quality, high-value biological reagents and solutions for global innovative pharmaceutical companies and research institutions. For more details about the "IGJ Recombinant Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody" or to request a sample test, please feel free to contact us.
Product Information
| Catalog Number | Product Name | Product Parameters |
| S0B0350 | S-RMab® IGJ Recombinant Rabbit mAb (S-342-48) | Host : Rabbit Conjugation: Unconjugated |
| S0B0051 | IGJ Recombinant Rabbit mAb (SDT-R128) | Host : Rabbit |
Related News
- Mouse T Cell Activation: A Systematic Guide to Developmental Differentiation and 3/12/2026
- Mouse T Cell Activation Kits: Enabling Efficient Immune Activation Through the C 3/11/2026
- Junshi Biosciences Announces NMPA Acceptance of New Drug Applications for Toripa 3/10/2026
- Rapport Therapeutics and Tenacia Biotechnology Announce Strategic Collaboration 3/10/2026
- Cas9 Antibodies: Ensuring Precision and Reproducibility in Gene Editing Research 3/10/2026
- Recombinant Rabbit Monoclonal Antibodies: Revolutionizing the Precision and Reli 3/9/2026
- Neural Research Antibodies: The Key to Unraveling the Mysteries of the Brain 3/8/2026
- The Key Role of CK-Pan Antibody in Cell Biology Research 3/7/2026
- Site-Selective Acetylation: Unlocking New Functional Horizons for Antibody Drugs 3/6/2026
- Lactylation Antibodies: Deciphering Novel Molecular Mechanisms of Metabolic Repr 3/5/2026


