| Description | Detection principle: This kit uses double antibody sandwich ELISA technology. Specific anti-Human IL-1β capture antibody was pre-coated on a high affinity enzyme plate. The standard substance, the sample to be tested and the biotin-labeled detection antibody are sequentially added to the wells of the enzyme labeled plate, and then thoroughly shaken and mixed, and then placed at room temperature for an incubation process for 2 hours. The IL-1β present in the sample is combined with the solid phase antibody and the detection antibody. After extensive washing to remove free and unbound components, horseradish peroxidase-labeled Streptavidin-HRP (SA-HRP) was added. After washing again, TMB chromogenic substrate was added and incubated at room temperature in the dark from light to develop color. The depth of color reaction was positively correlated with the concentration of IL-1β in the sample. The reaction was stopped by adding a stop solution, and the absorbance value was measured using a microplate reader at a detection wavelength of 450 nm (corrected wavelength of 570-630 nm).
Test Type:Double antibody sandwich method Form:Pre-coated 96-well plate Test Sample Type:Cell supernatant, serum, plasma Sample Load:100 μl Kit Components:A copy of the pre-coated 96-well plate, standard, IL-1β detection antibody, standard dilution, test buffer, TMB chromogenic substrate, wash solution, stop solution, SA-HRP, plate sealing membrane, and instructions. Sensitivity:0.15 pg/mL Detection range:3.91-250pg/ml Recovery Range:94-113% Save Method:2-8℃ Standard graph: 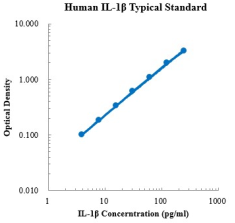 Background: Interleukin 1 (IL-1) is an extracellular polypeptide of 17 kDa, which is divided into two proteins: IL-1α and IL-1β. IL-1β is an activated form of a protein precursor secreted by activated macrophages produced by hydrolysis of caspase 1 (CASP1/ICE). This cytokine is an important mediator of the inflammatory response and is involved in many cellular activities, including cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. IL-1 is an important family of proteins, which are derived from biologically activated monocytes and participate in inflammatory and immune responses. Elevated IL-1β expression produces a variety of different autoinflammatory syndromes, most notably a single-gene condition called CAPS, caused by mutations in the inflammasome receptor NLRP3 that triggers IL-1β processing. |





