Reagents:
Molecular Biology
Biochemistry
Cell Biology
ELISA / Diagnostic Kits
Antibody
Serum/Medium
Other Reagents
- Human EGF ELISA Kit

- Product Detail
- Company Profile
Product Specification
| Usage | Need to bring your own test equipment 1. Microplate reader (can measure the absorption value of 450nm detection wavelength and the absorption value of 540nm or 570nm correction wavelength) 2. High-precision liquid dispenser and disposable tip 3. Distilled water or deionized water 4. Bottle washing (spray bottle), multi-channel plate washer or automatic plate washer 5. 500mL measuring cylinder 1. Preparation before the experiment 1. Sample collection and storage ① Cell culture supernatant: particulate matter should be removed by centrifugation; Test the sample immediately. If the sample is not tested in time after collection, it is recommended to pack it according to the one-time usage amount and store it in a refrigerator at-20 ℃ to avoid repeated freezing and thawing. Samples may need to be diluted with diluent (1 ×). ② Serum: Use a serum separation tube (SST) to collect samples, and place the samples at room temperature for 30 minutes. Centrifuge for 15 minutes at a rotation speed of 1000 g. The serum was removed immediately and tested immediately. If the sample is not tested in time after collection, it is recommended to pack it according to the one-time usage amount and store it in a refrigerator ≤-20 ℃ to avoid repeated freezing and thawing. Samples may need to be diluted with diluent (1 ×). ③ Plasma: Plasma was collected using EDTA, heparin or citric acid as anticoagulant, centrifuged for 15 minutes within 30 minutes after collection, rotated at 1000g, and detected immediately. If the sample is not tested in time after collection, it is recommended to pack it according to the one-time usage amount and store it in a refrigerator ≤-20 ℃ to avoid repeated freezing and thawing. Samples may need to be diluted with diluent (1 ×). 2. Reagent preparation (Please place all reagents and samples at room temperature before use and let them stand15Minutes. All experimental samples and standards are recommendedDo repeat hole detection) ① Preparation of 1 × washing liquid: The concentrated washing liquid in the kit is 20 × mother liquid, which needs to be diluted into 1 × working liquid with distilled water before use.Example:Take 10mL of concentrated washing solution + 190mL of distilled water and make the volume to 200mL. In actual operation, the amount used can be calculated first, and then prepared. ② Preparation of 1 × dilution buffer: The concentrated dilution buffer in the kit is 10 × mother liquor, and before use, it needs to be diluted to 1 × working liquid with distilled water.Example:Make up to 30 mL with 3 mL of concentration and dilution buffer + 27 mL of distilled water. In actual operation, the required amount of dilution buffer solution can be calculated according to the sample dilution factor, and then prepared. ③ Antibody detection: centrifuge the dry powder to the bottom of the tube, dissolve it with 110uL dilution buffer (1 ×), and let it stand at room temperature for 5 minutes to obtain 100 × mother liquor; Dilute to 1 × working solution before use. Calculate the required volume according to the dosage of 100uL per well.Example:After 10 wells were used, 10 uL of the detection antibody having a working concentration of 100 times was taken, and the volume was diluted to 1 mL using a dilution buffer (1 ×) to obtain 1 mL of the detection antibody having a working concentration of 1 ×. ④ SA-HRP: SA-HRP is 40 × mother liquor, which needs to be diluted with dilution buffer (1 ×) before use to prepare 1 × working solution, and the required amount per well is 100uL.Example:After 10 wells were used, 25 uL of 40 × mother liquor + 975 uL of dilution buffer (1 ×) was diluted to 1 mL to obtain 1 mL of detection antibody having a 1 × working concentration. ⑤ Color development solution: According to 100uL per well, calculate the dosage required for the current test, take out the corresponding volume of color development solution, and protect it from light; The chromogenic solution removed is for the same day only. ⑥ Standard: The freeze-dried standard is re-dissolved with dilution buffer (1 ×), and the re-dissolving volume is 1000uL to obtain the standard mother liquor with a concentration of 250pg/mL. Gently shake for at least 5 minutes and it dissolves well. 300 uL of dilution buffer (1 ×) was added to each dilution tube. Make serial dilutions of the standard mother liquor according to the figure below, and each tube must be thoroughly mixed before pipetting to the next tube. The standard mother solution without dilution can be used as the highest point of the standard curve (250 pg/mL), and the dilution buffer (1 ×) can be used as the zero point of the standard curve (0 pg/mL). 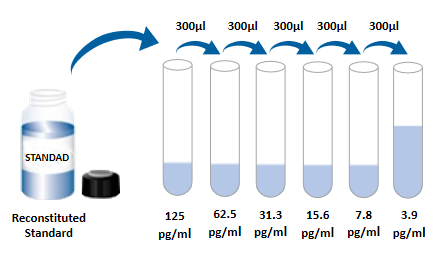 2. Operation steps 1. Prepare all required reagents and standards; 2. Take out the microplate from the sealed bag that has been balanced to room temperature. Please put the unused slats back into the aluminum foil bag and reseal them; 3. Add 300uL of washing liquid to the microplate, let it stand and soak for 30 seconds, discard the washing liquid and pat the microplate dry on absorbent paper. Please use it immediately and do not let the microplate dry; 4. Add different concentration standards, experimental samples or quality control products to the corresponding wells, 100uL per well. Sealing the reaction hole with plate sealing adhesive paper and incubating at room temperature for 2 hours; 5. Suck off the liquid in the plate and wash the plate with a bottle washer, a multi-channel plate washer or an automatic plate washer. 300 uL of washing solution was added to each well, and then the washing solution in the plate was aspirated off. Repeat the operation 3 times. Trying to absorb the residual liquid as much as possible every time you wash the plate will help to get good experimental results. At the end of the last plate washing, please suck all the liquid in the plate or turn the plate upside down, and pat all the residual liquid dry on absorbent paper; 6. Add 100 uL of detection antibody to each well. Seal the reaction wells with plate sealing tape and incubate at room temperature for 2 hours; 7. Repeat the plate washing operation in step 5; 8. Add 100uLSA-HRP to each well and incubate at room temperature for 20 minutes. Be careful to avoid light; 9. Repeat the plate washing operation in step 5; 10. Add 100uL of chromogenic solution to each microwell, incubate at room temperature for 5-30 minutes, and avoid light; 11. Add 50uL of stop solution to each microwell, and the color of the solution in the well will change from blue to yellow. If the color of the solution changes to green or the color changes are inconsistent, pat the microplate gently to mix the solution evenly; 12. Within 30 minutes after adding the stop solution, measure the absorbance value of 450nm using a microplate reader, and set 540nm or 570nm as the calibration wavelength. If dual-wavelength correction is not used, the accuracy of the results may be affected; 13. Calculation Results: Average the corrected absorbance values (OD450-OD540 or OD570), multiple well readings for each standard and sample, and then subtract the average zero standard OD value. Four-parameter logic (4-PL) curve fitting was performed using computer software to create the standard curve. Alternatively, a curve can be generated by plotting the logarithm of the standard concentration versus the logarithm of the corresponding OD value, and the best fit line can be determined by regression analysis. This process can generate a data fit that is sufficiently useful but less accurate. If the sample is diluted, the concentration should be calculated by multiplying the dilution factor.  3. Kit parameters 1. Recovery rate: Different levels of Human EGF were spiked into cell culture medium samples and the recovery rate was determined. The recovery range is 96-103%, and the average recovery is 99%. 2. Sensitivity: The lowest measurable dose (MDD) of Human EGF is generally 0.089-0.740 pg/mL. The lowest measurable value is the corresponding concentration calculated from the mean of the zero-point absorbance values of 20 standard curves plus two standard deviations. 3. Calibration: This ELISA kit was calibrated with high purity recombinant Human EGF protein expressed by sf-21 insect cells. 4. Linearity: 4 different samples were spiked with high concentrations of Human EGF, and then the samples were diluted to the detection range with diluent (1 ×) to determine their linearity.
5. Specificity: This ELISA method can detect natural and recombinant Human EGF protein. The following factors were formulated with diluent (1 ×) at a concentration of 50 ng/mL to detect cross-reactivity with Human EGF. Interference with Human EGF was detected by incorporating 50 ng/mL of interfering factor into the mid-range recombinant Human EGF control. No significant cross-reactivity or interference was observed. Cross-reacted approximately 2.3% with recombinant Human Pro-EGF. < tdstyle = "width: 24.0691%; text-align: center; height: 22px;" > EGF R
4. Analysis of frequently asked questions 1. Whiteboard (after the color development is completed, no color appears)
2. Flower plate (blank and negative positive controls are normal, but the OD value of specimen wells is obviously higher)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Species Reactivity | Human | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Theory | This kit adopts double antibody sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent detection technology. Specific anti-human EGF antibodies were pre-coated on high affinity plates. The standard substance, the sample to be tested and the biotinylated detection antibody are added to the well of the enzyme label plate, and after incubation, the EGF present in the sample combines with the solid phase antibody and the detection antibody to form an immune complex. After washing to remove unbound material, horseradish peroxidase-labeled Streptavidin-HRP was added. After washing, a chromogenic substrate is added to protect the color from light. A stop solution was added to stop the reaction, and the absorbance value was measured at a wavelength of 450 nm (reference calibration wavelength of 540 nm or 570 nm). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonym | Human epidermal growth factor ELISA kit, beta-Urogastrone, EGF, epidermal growth factor (beta-Urogastrone), epidermal growth factor, HOMG4, pro-epidermal growth factor, URG, Urogastrone | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Composition | Please use within the expiration date of the kit
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Background | The EGF (epidermal growth factor, also known as Urogastrone) precursor is a Group I member of the EGF family of growth factors with a molecular weight of 185kDa. Group I members are molecules that bind and activate the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). EGF family members are synthesized as type I transmembrane (TM) proteins and are proteolyzed to a soluble form. Human epidermal growth factor (EGF) is a fragment in the form of a 1185 amino acid precursor molecule, containing 1010 amino acid extracellular region, 21 amino acid TM region and 153 amino acid cytoplasmic domain. The extracellular domain (ECD) of this precursor has three main structural modules. These include nine BLDLR repeats, one von Willebrand factor A region, and nine EGF-like repeats, and contain the 53 amino acid structure of the mature EGF molecule in the proximal membrane region (amino acids 971 to 1023 of the precursor form). This transmembrane 185kDa isoform (amino acids 21-1023) is found in most body fluids. This process also produces a large number of protein fragments of 40-100kDa, which may be proteolytic degradation products. The production process of 6kDa mature EGF isoforms is unknown. It may originate inside the cell or on the cell surface by hydrolysis of a soluble 160 kDa precursor or a 70 kDa molecular isoform produced after hydrolysis of this precursor by membrane-bound serinase on the cell surface. Notably, the mature form of EGF, the 185 kDa transmembrane protein, the circulating molecule that has been hydrolyzed but not yet processed, and the 160 kDa precursor molecule are all biologically active. These biological activities are mainly due to the embedding of EGF peptides in these precursor molecules. Modifications of other types of EGF do not have the activity to bind to EGF receptors. There are four possible splice bodies in the expression of EGF protein in the gene encoding EGF, but none of them affect the sequence of mature EGF. Two of these splicers occurred in the extracellular region sequence, deleting amino acids from positions 913 to 953 and amino acids from positions 314 to 355, respectively. The other two splicebodies involve the intracellular region of EGF, replacing amino acids from positions 1125 to 1207 with 12 amino acids and amino acids from positions 1136 to 1207 with 17 amino acids, respectively. The homology of mature human EGF to mouse, rat and pig EGF is 70%, 70% and 85%, respectively. Cells known to express EGF include platelets, cerebral neurons, astrocytes and cerebellar Purkinje cells, Bruner cells (duodenum) and submandibular gland cells, unstained ciliated epithelium, and anterior pituitary cells. EGF has many different physiological effects. At present, the widely recognized function of EGF is mainly based on the binding of EGF receptor-ligand. EGF receptors can also bind to other EGF family proteins, thereby forming heteromultimers and dimerizing with other EGF receptor family members, or associating with other transmembrane proteins such as PDGFR and HGF receptors. In either case, EGF can have an effect on fetal and adult tissues. In the fetus, EGF affects thymocyte growth and differentiation during the double-negative-double-positive stage. During neuronal formation, EGF also appears to stimulate the generation of glial neurons and promote their epithelialization. Finally, it inhibits the maturation of fat cells, thus increasing the preadipocyte count. In adults, EGF can play a role in the milk production process of mammary gland, and can also cause fibroblast mitosis, ECM dissociation and migration, and widely affect various effects related to growth factors. The mechanism of activation of EGF receptors, epidermal growth factor receptors (also known as HER1 and ErbB1), is unclear. Current research believes that each EGF molecule and an EGF receptor molecule have two binding sites, which will force the receptor to undergo conformational changes and bind to the second EGF-EGFR complex. This dimer is the EGF receptor with actual function. ErbB2 can also form heterodimers with the EGF receptor, but cannot bind to EGF. This may be because ErbB2 naturally exists as a dimer, which masks its ligand binding site, so that the ligand cannot bind to it. Therefore, it needs to bind an already activated EGF-EGFR complex to form a functional EGF receptor. However, due to the intrinsic electrostatic repulsion, ErbB2 itself cannot form homodimers. EGF can also form heteromultimer with ErbB3: ErbB2 only at high concentrations. The importance of this process is still unknown. Alternatively spliced isoforms of EGFR are present in tumor cells and may be involved in tumorigenesis or sensitize cells to EGF receptor inhibitors. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General Notes | 1. Please use the kit within the validity period. 2. The components of different kits and different batch kits cannot be mixed. 3. If the sample value is greater than the highest value of the standard curve, the sample should be diluted with diluent (1 ×) and re-tested; If the cell culture supernatant sample needs to be distributed and diluted, cell culture medium can be used for other intermediate dilutions except dilution with diluent in the last step. 4. Differences in test results can be caused by a variety of factors, including the operation of the experimenter, the use of the pipette, the plate washing technique, the reaction time or temperature, the storage of the kit, etc. 5. The terminating solution in the kit is an acidic solution. Please protect your glasses, hands, face and clothes when using it. 6. For scientific research only, not for in vitro diagnosis. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Storage Temp. | Kit unopened, stored at 2-8 °C. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Test Range | 3.9pg/mL-250pg/mL |
bio-equip.cn
-
AntBio is a biotechnology group company dedicated to serving life sciences, aiming to help scientists accelerate research and improve work efficiency. AntBio provides comprehensive and high-quality reagent tools for basic research, drug development, and diagnosis, including research grade antibodies, proteins, biochemical reagents, and assay kits. These research tools are widely used in different segments of life science research. The group company currently consists of three brands, Absin, Starter-Bio and UA-Bio.
| Request Information |
| Other Products |
| Related Products |
| Recently viewed products |
- SiteMap



