| Usage | Required equipment and reagents:
1. Microplate reader (wavelength 450nm filter)
2. 37 °C incubator (CO for cells is not recommended2Incubator)
3. Automatic plate washing machine or multi-channel pipette/5ml dropper (for manual plate washing)
4. Precise single-channel (0.5-10μL, 5-50μL, 20-200μL, 200-1000μL) and multi-channel pipettes (the pipette needs to be calibrated before use).
5. Sterile EP tube and disposable tip
6. Absorbent paper and sample loading tank
7. Deionized water or distilled water
Sample collection and storage:
1Serum,
Whole blood samples were left at room temperature for 2 hours or overnight at 2-8 °C. Centrifuge at 1000 × g for 20 minutes and remove the supernatant. Can be tested immediately or frozen at-20 °C or-80 °C in single-use packages.
2Plasma,
It is recommended to use EDTA-Na2/K2 as an anticoagulant. Centrifuge at 2-8 °C and 1000 × g for 15 minutes within 30 minutes after sample collection, and take the supernatant. Can be tested immediately or frozen at-20 °C or-80 °C in single-use packages.
3Tissue samples,
Tissue samples are generally made into tissue homogenates, and the processing methods are as follows:
(1) Place the target tissue on ice, wash it with pre-cooled PBS buffer (0.01 M, pH = 7.4) to remove residual blood, weigh it and use it later.
(2) Grind the tissue homogenate with lysate on ice. The volume of lysate added depends on the weight of the tissue, and typically 9 ml of lysate is used per 1 g of tissue fragment. In addition, it is recommended to add a protease inhibitor, such as 1 mM PMSF, to the lysate.
(3) Ultrasonic crushing or repeated freezing and thawing can be used for further treatment (during the ultrasonic crushing process, ice bath cooling is required; the repeated freezing and thawing method can be repeated twice).
(4) Centrifuge the prepared homogenate at 5000 × g for 5 minutes, and retain the supernatant for detection. Or frozen at-20 °C or-80 °C in single-use packages.
(5) According to the needs of the experiment, the total protein concentration of tissue homogenate samples can be measured first to facilitate data analysis. BCA method is recommended. Generally, the total protein concentration is adjusted to 1-3 mg/ml for ELISA detection. Some tissue samples, such as liver, kidney and pancreas, contain high concentrations of endogenous peroxygenase, which will react with chromogenic substrates at high sample concentrations, resulting in false positives. 1% H may be attempted2O2Inactivate for 15 minutes and then detect.
Note: Commonly used lysatePBSBuffer, or use moderate strengthRIPALysate. UsingRIPAWhen lysing solution,PHThe value needs to be adjusted toPH7.3, avoid using containingNP-40,Triton X-100AndDTTThe components will seriously inhibit the work of the kit. Recommended use50 mM Tris+0. 9% NaCL+0. 1% SDS, PH 7.3。
4Cell culture supernatant,
The supernatant was collected, centrifuged at 2-8 ° C. at 2500 rpm for 5 min, and the clear cell culture supernatant was collected. Use immediately for testing, or freeze at-80 °C as a single-use quantity.
5Cell lysate,
(1) Collection and lysis of suspended cells: centrifuge at 2-8 °C and 2500 rpm for 5 minutes to collect the cells. Add pre-cooled PBS, gently mix and wash, centrifuge at 2-8 °C at 2500 rpm for 5 minutes, and collect the cells. Add 0.5-1ml cell lysate and appropriate amount of protease inhibitor (such as PMSF, working concentration 1mmol/L), put on ice, lyse for 30min-1h, or disrupt with ultrasonic waves.
(2) Collection and lysis of adherent cells: aspirate the supernatant and add pre-cooled PBS to wash three times. Add 0.5-1 ml of cell lysate and an appropriate amount of protease inhibitor (such as PMSF, working concentration 1 mmol/L), and gently scrape off the adherent cells with a cell scraper. The cell suspension was transferred into a centrifuge tube, placed on ice, lysed for 30 min-1 h, or disrupted by ultrasonic waves.
(3) During the cell lysis process, the centrifuge tube can be blown with the gun tip or shaken intermittently to fully lyse the protein, and the sticky appearance is DNA. Ultrasonic waves can be used to break the DNA. (Or use ultrasonic 3-5mm probe, power 150-300W, ultrasonic treatment sample on ice, work for 1-2 seconds, stop for 30 seconds, 3-5 cycles.)
(4) After lysis or ultrasonic disruption is completed, centrifuge at 2-8 °C at 10000rpm for 10min, and transfer the supernatant into an EP tube for detection immediately, or pack it at-80 °C for frozen storage according to the amount used once.
Note: The precautions are the same as for tissue samples.
6Other biological samples
Samples were centrifuged at 1000 × g for 20 minutes at 2-8 °C. The supernatant is collected for testing immediately, or frozen at-80 °C as a single-use amount. Other precautions for samples:
1. The test tube for collecting blood should be a disposable endotoxin-free test tube. Avoid the use of hemolyzed, hyperlipidemic samples.
2. Optimal storage conditions for samples: 2-8 °C should be stored for less than 5 days,-20 °C should not exceed 6 months,-80 °C should not exceed 2 years, and should be stored in liquid nitrogen beyond the above time. When the frozen specimen is thawed, in order to reduce the damage of ice crystals (0 °C) to the sample, it should be quickly thawed in a 15-25 °C water bath. After thawing, the sediment should be removed by centrifugation, and then mixed for testing.
3. The detection range of the kit is not equal to the concentration range of the substance to be tested in the sample. If the concentration of the test substance in the sample is too high or too low, please dilute or concentrate the sample appropriately.
4. If the sample tested is special and there is no reference data, it is recommended to conduct pre-experiments to verify its effectiveness.
5. The recombinant protein may not match the capture or detection antibody in the kit and cannot be detected.
Recommended sample dilution protocol:
The following table shows that this kit is aimed atLimited sampleThe recommended dilution ratio is for reference only. (ND is not detected) | Sample Type | Recommended dilution ratio | Reference content | | Healthy serum | 1/2 dilution | 0-72 pg/ml | | A549 cell culture supernatants (10 μg/mL poly I: C stimulation for 24 hours) | undiluted | 1162 pg/ml |
The matrix components in serum/plasma will affect the test results and need to be diluted at least 2 times (1/2) with sample diluent!
If your model group sample requires a different dilution ratio, please refer to the following general dilution scheme (this scheme is a dilution scheme without double wells for testing. When double wells need to be set, please add the sample and diluent volume x the number of double wells):
Dilution 2-fold (1/2): One-step dilution. Add 60ul of sample to 60ul of sample diluent and mix gently.
Dilution 5-fold (1/5): One-step dilution. Add 24ul of sample to 96ul of sample diluent and mix gently.
Dilution 10-fold (1/10): One-step dilution. Add 12ul of sample to 108ul of sample diluent and mix gently.
Dilution 20-fold (1/20): One-step dilution. Add 6ul of sample to 114ul of sample diluent and mix gently.
Dilution 50-fold (1/50): One-step dilution. Add 3ul sample and 47ul normal saline (i.e. 0.9% sodium chloride) to 100ul sample diluent and gently mix well.
Dilution 100-fold (1/100): One-step dilution. Add 3ul sample and 177ul normal saline to 120ul sample diluent and gently mix well.
Dilution 1000 times (1/1000): Two-step dilution, you can dilute 50 times first (this step is all diluted with normal saline), and then dilute 20 times. Gently mix well.
Dilution 10000 times (1/10000): Two-step dilution, you can dilute 100 times first (this step is all diluted with normal saline), and then dilute 100 times. Gently mix well.
Dilution 100,000 times (1/100000): Three-step dilution, you can first dilute 50 times, then dilute 20 times (the first two steps are all diluted with normal saline), and finally dilute 100 times. Gently mix well.
Note: The amount of liquid taken during each dilution step is not less than3ul, the dilution factor is not more than100Times. Each step of dilution should be mixed evenly to avoid foaming.
Pre-test reagent preparation:
Remove the kit from the refrigerator 20 minutes in advance and equilibrate to room temperature (18-25 °C). If the kit needs to be used multiple times, please take out only the enzyme-labeled slats and standards required for this experiment, and store the remaining enzyme-labeled slats and standards according to the specified conditions.
1Lotion,:
30 ml of concentrated wash solution (15 ml for 48T) was diluted to 750 ml (375 ml for 48T) with deionized water or distilled water (ultrapure water with a recommended resistivity of 18 MΩ) and mixed well. Or according to the requirements of the experiment, take an appropriate amount of concentrated washing solution to dilute to 25 times the volume and mix well, and return the unused solution to 2-8 °C.
If crystals are formed in the concentrated wash liquid, it can be heated in a 40 ° C. water bath (the heating temperature should not exceed 5 ° C.)0 °C) until the crystals are completely dissolved, mix well and use. The prepared lotion is best used on the same day. If it can't be used up, it can be stored at 2-8 °C for no more than 48 hours.
2Standard,:
(1) Centrifuge the lyophilized standard tube at 10000 × g for 1 minute. Marked as Zero tube.
(2) Take 1mL of sample diluent and add it to the freeze-dried standard product tube, tighten the cap of the tube, let it stand at room temperature for 2 minutes, and gently mix it upside down several times (or add 1mL of sample diluent and let it stand for 1-2 minutes, mix with a low-speed vortex machine for 3-5 seconds). Centrifuge at 1000 × g for 1 minute at low speed and collect the liquid to the bottom of the tube.
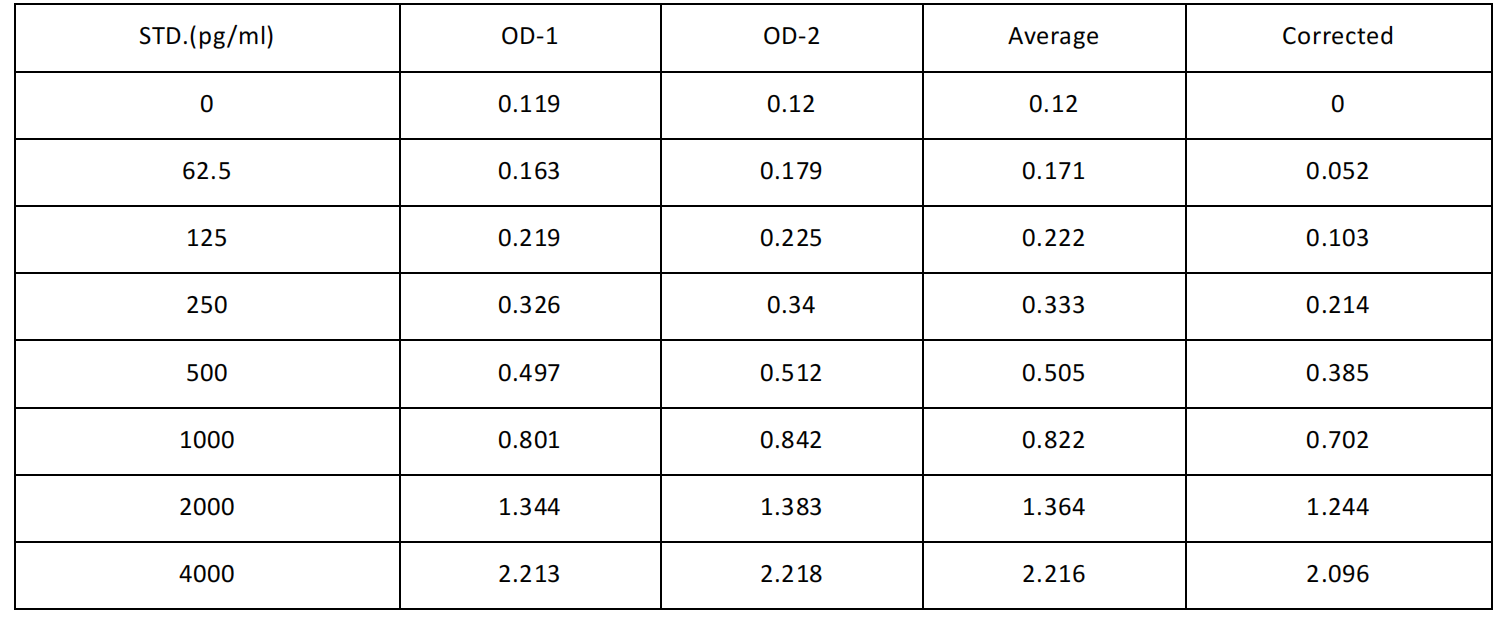
(3) Gradient dilution: another seven EP tubes were taken and labeled 1/2, 1/4, 1/8, 1/16, 1/32, 1/64 and blank. First, 0.3 ml of sample dilution was added to each EP tube. Add 0.3 ml of Zero tube standard solution to 1/2 tube and mix thoroughly. Take 0.3 ml 1/2 tube standard solution into 1/4 tube and mix thoroughly. Take 0.3 ml of 1/4 tube standard solution into 1/8 tube, mix thoroughly, and so on. Note that there is only sample dilution in the Blank EP tube. At this time, the concentrations of standards in the eight EP tubes from the Zero tube tube to the blank tube were 4000 pg/ml, 2000 pg/ml, 1000 pg/ml, 500 pg/ml, 250 pg/ml, 125 pg/ml, 62.5 pg/ml, and 0 pg/ml, respectively.
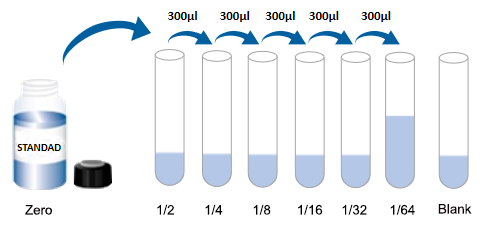
Note:Dissolved tube zero standard, please store in2-8 °C, and in12Use within hours. For other diluted gradient standard working solution, please refer to2Use within hours.
3Biotin,-Antibody working solution:
Prepare it within 30 minutes before the experiment, use it now, and it is not suitable for long-term storage.
(1) Calculate the total volume of required working fluid: 100ul/hole × number of holes. (It is preferable to prepare an amount of 100 ul-200 ul more than the total volume)
(2) Centrifuge at 1000 × g at low speed for 1 minute, and collect the concentrated biotin-antibody to the bottom of the tube.
(3) Dilute the concentrated biotin-antibody with the antibody diluent at the ratio of 1/100, and mix well. (e.g. 10 ul of concentrated biotin-antibody is added to 990 ul of antibody dilution)
4、HRP-Streptavidin(SABC)Working fluid:
Prepare it within 30 minutes before the experiment, use it now, and it is not suitable for long-term storage.
(1) Calculate the total volume of required working fluid: 100ul/hole × number of holes. (It is preferable to prepare an amount of 100 ul-200 ul more than the total volume.)
(2) Centrifuge at 1000 × g at low speed for 1 minute, and collect the concentrated SABC to the bottom of the tube.
(3) Dilute and concentrate SABC with SABC diluent at the ratio of 1/100, and mix well. (e.g. 10 ul of concentrated SABC is added to 990 ul of SABC dilution) Summary of operation steps:
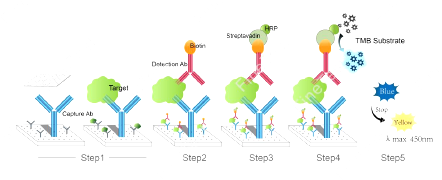
procedure1:Add 100 ul of standard or sample to be tested to the wells, apply a coating film, and incubate at 37 ° C. for 90 minutes.
Plate washing:Wash the plate 2 times. No soaking.
procedure2:100 ul of biotin-antibody working solution was added, coated, and incubated at 37 ° C. for 60 minutes.
Plate washing:Wash the plate 3 times. Soak for 1 minute at a time.
procedure3:100 ul of HRP-streptavidin (SABC) working solution was added, coated, and incubated at 37 ° C. for 30 minutes.
Plate washing:Wash the plate 5 times. Soak for 1 minute at a time.
procedure4:90 ul of TMB chromogenic substrate was added. Apply the coating film and incubate at 37 ° C. for 10-20 minutes (please use the TMB color development precision control method).
procedure5:50 ul of the reaction stop solution was added. The OD450 value was immediately read at 450 nm and calculated. Detailed operation steps:
When diluting samples and reagents, they should be thoroughly mixed. It is recommended that a standard curve be plotted for each test.
1. Set standard wells, sample wells and blank wells, and record their positions. In order to reduce the experimental error, it is recommended to set up double holes for standards and samples.
2、Loading:Add 100ul of each gradient standard to the standard wells, add 100ul of moderately diluted sample to be tested to the sample wells, and add 100ul of sample dilution to the blank wells. The film was applied and incubated at 37 ° C. for 90 minutes. (Add the solution to the bottom of the microplate, gently shake and mix well, avoiding contact with the tube wall and blistering as much as possible.)
3、Washing plate2Times:Remove the coating film, suck off or shake off the liquid in the enzyme labeled plate, and pat it on clean absorbent paper 2-3 times. Add 350ul of washing buffer to each well, do not soak, discard the liquid in the well, and pat it on absorbent paper 2-3 times. Repeat this plate washing step twice.
4、Plus biotin-Antibody working solution:100 ul of biotin-antibody working solution was added to each well. The film was applied and incubated at 37 ° C. for 60 minutes.
5、Washing plate3Time:Remove the coating film, suck off or shake off the liquid in the enzyme labeled plate, and pat it on clean absorbent paper 2-3 times. Add 350ul of washing buffer to each well, soak for 1 minute, discard the liquid in the well, and pat 2-3 times on absorbent paper. Repeat the plate washing step 3 times.
6、AddHRP-Streptavidin(SABC):Add 100ul of SABC working solution to each well. The film was applied and incubated at 37 ° C. for 30 minutes. (While equilibrating the whole bottle of TMB in a 37 ° C. incubator)
7、Washing plate5Times:Remove the coating and wash the plate 5 times with washing buffer. Refer to step 5 for the method.
8、AddTMBChromogenic substrate:90 ul of TMB chromogenic substrate was added to each well, coated, and incubated for 10-20 minutes at 37 ° C. protected from light. Turn on the microplate reader and preheat for 15 minutes. (Note: Do not use loading tanks for formulating HRP conjugates. Color development depending on the actual change of color, the reaction time can be shortened or extended, but not more than 30 minutes. When a good blue gradient appears in the standard well, the reaction can be terminated.
9、Add reaction stop solution:After color development, the liquid in the well should not be discarded, and 50ul of reaction stopping solution should be added to each well. The color will change from blue to yellow immediately. The stop solution was added in the same order as the TMB substrate was added.
10、ODMeasurement of values:The OD450 value was immediately read at 450 nm with a microplate reader. (If your plate reader has a selectable calibration wavelength, set it to 570nm or 630nm. The calibration read is the value of OD450 minus the value of OD570 or OD630. This method corrects and removes the OD value of non-chromogenic substances, thus obtaining a more accurate test result. If the plate reader does not have a wavelength of 570nm or 630nm, the original OD450 value can be used.) Results Calculation: 1. Take the average OD450 value of the standard and sample duplicate wells (using the original OD450 value or the corrected reading value), and then subtract the OD450 value of the blank well as the calculated value.
2. With the concentration as the abscissa and the OD450 value as the ordinate, you can use the four-parameter equation 4PL to draw the standard curve (the value of the blank hole is removed when drawing). You can also use the mapping software that comes with the microplate reader (such as Thermo FC model microplate reader SkanIt RE software), or Curve Expert 1.3 or 1.4 professional software to draw the standard curve.
3. Substitute the OD450 value of the sample into the standard curve to calculate the concentration value of the sample. If the sample has been diluted, multiply it by the corresponding dilution factor. Description of different methods for drawing standard curves:
1. Linear graph: one coordinate axis represents the concentration of antigen, and the other represents the read OD450 value. The R 2 value is generally used here to determine the fit, with a value greater than 0.99 indicating a very good fit. However, linear plots tend to compress the data points on the lower end of the curve, resulting in inaccurate calculation results.
2. Semi-logarithmic graph: helps to offset the lower end compression caused by linear graph. Semi-logarithmic plots use the logarithm of concentration versus readings. This approach typically results in sigmoidal curves with a more uniform distribution of data points.
3. Logarithmic/double logarithmic plot: Provides good linearity for low to medium concentration range. But the high end of the range tends to lose linearity.
4. Four-or five-parameter equation (4PL or 5PL) curve: The method is more complex and takes into account other parameters, such as maximum and minimum values, so it requires more complex calculations.
Whereas 4PL assumes symmetry around the inflection point, 5PL considers asymmetric cases and is generally more suitable for immunoassays. If your software allows, 4-PL and 5-PL will work for most ELISA calibration standard curves. Experimental data and standard curve:
This product has been tested by the quality control department and meets the performance requirements of the instruction manual. (Laboratory humidity 20%-60%, temperature 18 °C-25 °C. Equilibrate TMB to 37 °C before color development, and protect 37 °C from light after adding the plate wellsIncubate for 15 min.)
Due to differences in specific experimental environment and operation, the following experimental data and standard curves are for reference only, and experimenters need to establish standard curves according to their own experiments.
 Precision:
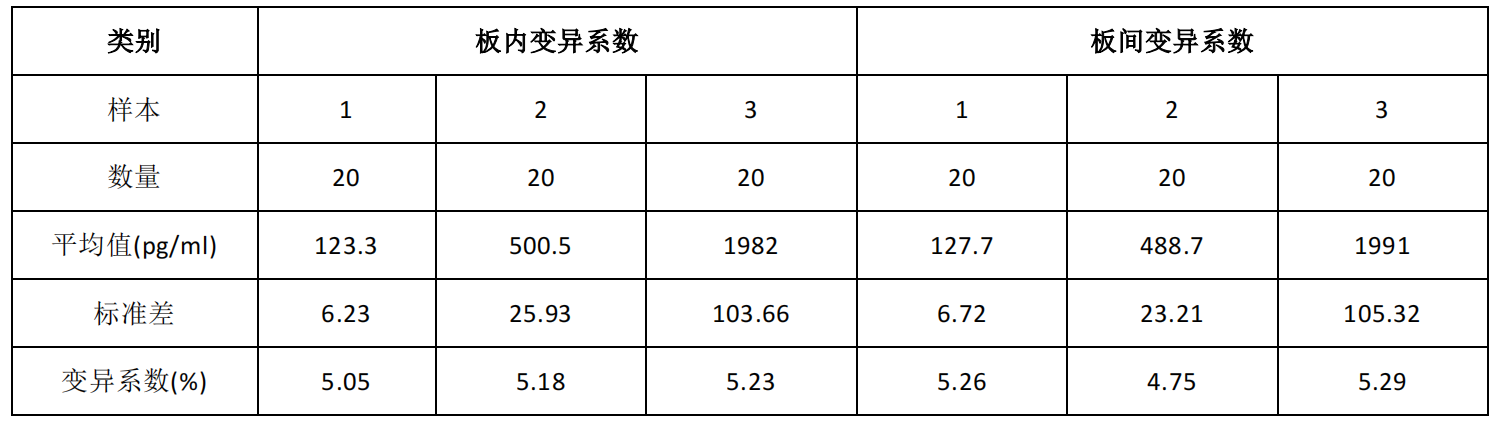
In-plate precision: Low, medium and high concentration samples were detected 20 times on the same enzyme labeled plate.
Inter-plate precision: Low, medium and high concentration samples were detected 20 times on 3 enzyme labeled plates respectively.
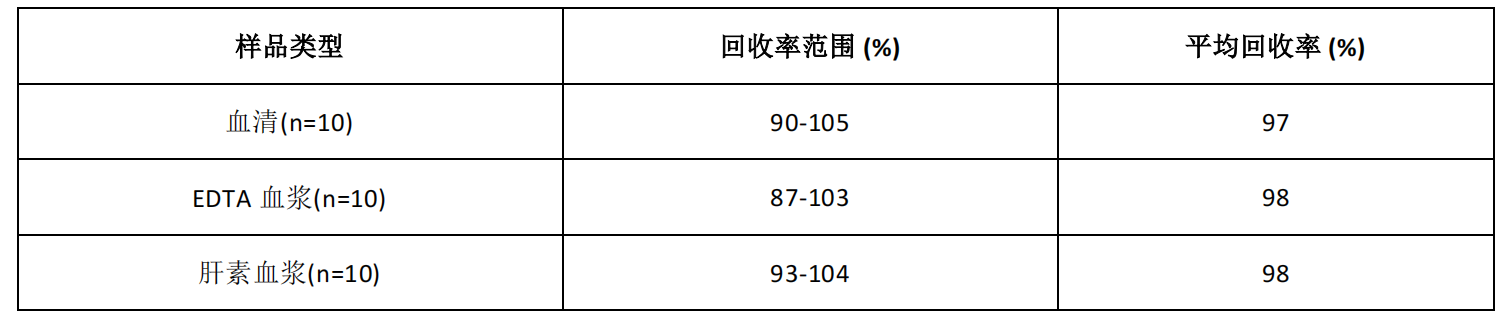
 Recovery:
An amount of IFN-β was added to the sample and the recovery was calculated by comparing the measured value to the expected amount of IFN-β in the sample.
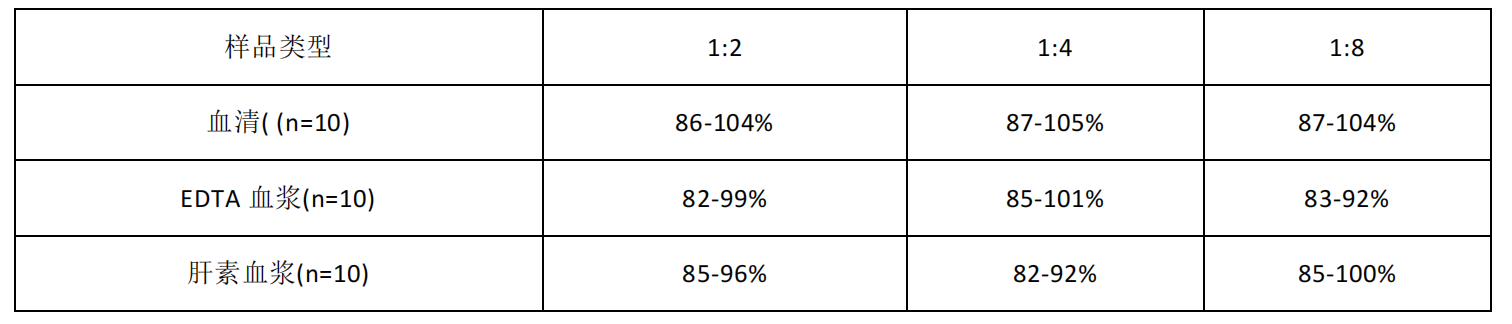
 Linearity:
The samples added with appropriate concentrations of IFN-β were diluted 2-fold, 4-fold, and 8-fold respectively for detection, and the recovery range was obtained.
 |










