| Description | Detection Principle: This kit uses double antibody sandwich ELISA technology. Specific anti human LIF capture antibody was pre coated on a high affinity microplate. Add the standard and the sample to be tested into the wells of the enzyme plate, shake well and mix well, and then place it at room temperature for 2 hours of incubation process. The LIF existing in the sample binds to the solid-phase antibody. After thorough washing to remove unbound components, biotinylated detection antibody was added for incubation. After washing again, streptavidin HRP (sa-hrp) labeled with horseradish peroxidase was added. After thorough washing again, TMB chromogenic substrate was added to avoid light for color development. The depth of color response has a positive correlation with the concentration of LIF in the sample. Add stop solution to stop the reaction, and use a microplate reader to measure the absorbance value under the condition of 450 nm detection wavelength (correction wavelength 570-630 nm). Detection Type: Double antibody sandwich method Form: pre coated 96 well plate Test Sample Type: cell supernatant, serum, plasma Loading Amount: 100 μ L Kit Components: A copy of pre coated 96 well plate, standard, LIF detection antibody, standard dilution, detection buffer, TMB chromogenic substrate, washing solution, termination solution, sa-hrp, plate sealing membrane and instructions. Sensitivity: 0.64pg/ml Detection Range: 15.63-1000 pg/ml Recovery Range: 81-117% Storage Method: 2-8 ℃ Standard Curve: 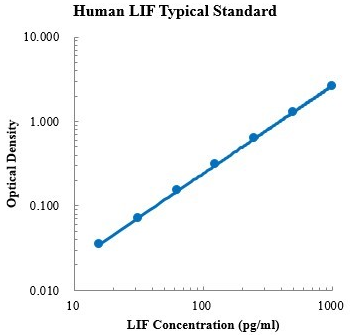
Background: Leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF)It is an interleukin-6 family cytokine that affects cell growth by inhibiting differentiation. When LIF levels decrease, cells differentiate. Activated T cells, monocytes, astrocytes, osteoblasts, keratinocytes, mast cells, and fibroblasts can all express lif. LIF is named for its ability to induce terminal differentiation of myeloid leukemia cells and prevent the continuous growth of leukemia cells. Other properties of LIF include promoting growth, promoting the differentiation of different types of target cells, affecting bone metabolism, cachexia, neural development, embryonic development and inflammation. LIF is involved in the process of endometrial decidualization and embryo implantation into the endometrium during pregnancy. When the levels of LIF and other cytokines in women drop, they are prone to pregnancy, but the risk of unexplained recurrent abortion will increase. Studies have shown that recombinant human LIF may help improve the implantation rate of female unexplained infertility. In addition, LIF is usually added to stem cell culture medium to reduce spontaneous differentiation. |





