| Description | Principle of detection:
The double antibody sandwich ELISA technique was used in this kit. Specific anti human growth hormone / GH capture antibodies were precoated on high affinity microplate plates. Microplate wells were supplemented with standards and samples to be tested, shaken well to mix and placed at room temperature for a 2-hour incubation, with growth hormone / GH present in the sample bound to the solid-phase antibody. After extensive washing to remove unbound components, biotinylated detection antibody was added for incubation. After another wash, horseradish peroxidase labeled streptavidin (streptavidin HRP, SA-HRP) was added. After another extensive wash, TMB chromogenic substrate was added and color was developed protected from light. The depth and lightness of the color reaction had a positive correlation with the concentration of Growth Hormone / GH in the sample. The reaction was stopped by adding stop solution, and the absorbance values were determined using a microplate reader at 450 nm detection wavelength (corrected wavelength 570-630 nm). Type of detection: double anti sandwich assay
Format:pre coated 96 well plates
Test sample type:cell supernatant, serum, plasma
Loading: 100 μ l
Kit components:pre coated 96 well plates, standards, GH detection antibodies, standard dilutions, assay buffer, TMB chromogenic substrate, wash buffer, stop solution, sa-hrp, plate sealing membrane and one copy of the instructions.
Sensitivity:0.62 pg / ml
Detection range:62.5-4000 pg / ml
Recovery range:80-124%
Method of preservation:2-8 ° C
Standard curve plots: 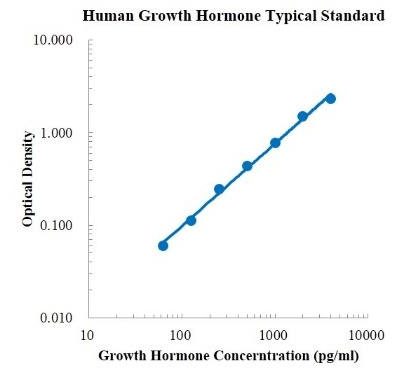 Background:
In humans and other animals, growth hormone (Growth Hormone / GH) stimulates growth, cell reproduction, and cell regeneration. Therefore it is important for human development. Growth hormone is a stress hormone that elevates the concentrations of glucose and free fatty acids. It also promotes IGF-1 production. The most common condition of growth hormone excess is pituitary tumor. The effects produced by growth hormone deletion differed by age. For young children, growth arrest and short stature are the main manifestations of growth hormone deficiency, often due to genetic factors and congenital malformations. It can also lead to delayed sexual maturation. In adults, GH deficiency is rare, most commonly due to pituitary tumors, other causes including continuation of GH deficiency in childhood, other structural damage or trauma, and extremely rare cases of idiopathic GH deficiency (GHD). |





