| Description | Detection Principle: This kit uses double antibody sandwich ELISA technology. The specific anti-human IL-5 capture antibody was pre coated on a high affinity microplate. Add the standard, the sample to be tested and the biotin labeled detection antibody into the wells of the enzyme plate in turn, shake well and mix well, and then place it at room temperature for 2 hours of incubation process. The IL-5 in the sample combines with the solid-phase antibody and the detection antibody. After washing sufficiently to remove free and unbound components, streptavidin HRP (sa-hrp) labeled with horseradish peroxidase was added. After washing again, TMB chromogenic substrate was added and incubated at room temperature in the dark to develop color. The depth of color response is positively correlated with the concentration of IL-5 in the sample. Add stop solution to stop the reaction, and use a microplate reader to measure the absorbance value at 450 nm detection wavelength (correction wavelength 570-630 nm). Detection Type: Double antibody sandwich method Form: pre coated 96 well plate Test Sample Type: cell supernatant, serum, plasma Loading Amount: 100 μ L Kit Components:A copy of pre coated 96 well plate, standard, IL-5 detection antibody, standard dilution, detection buffer, TMB chromogenic substrate, washing solution, termination solution, sa-hrp, plate sealing membrane and instructions. Sensitivity: 0.76pg/ml Detection Range: 15.63-1000 pg/ml Recovery Range: 91-107% Storage Method: 2-8 ℃ Standard Curve: 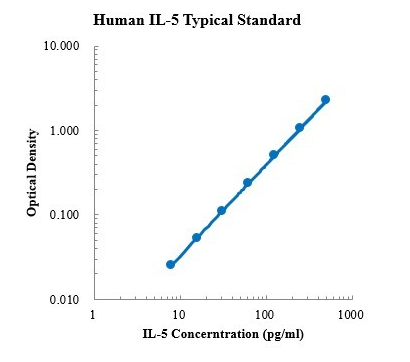
Background: Interleukin 5 (IL-5) is a Th2 cytokine member of hematopoietic family, which is composed of 115 amino acids. It is similar to other members of this cytokine family (IL-3 and GM-CSF)Different, the activated form of this glycoprotein is homodimer. IL-5 is secreted by Th2 cells and mast cells. Its biological activity on B cells and other types of cells shows that IL-5 has an important functional effect on the activity of Th2 cells. IL-5 stimulates B cell growth and increases immunoglobulin secretion by binding to its receptor. It is also a key factor in activating eosinophils. IL-5 has been associated with a variety of allergic diseases, including allergic rhinitis and asthma. A large increase in IL-5 was observed in circulating tissues and tracheal tissues, while sputum eosinophils decreased. |





