Home > News > Can c-Met Antibodies Become a New Hope for Tumor Targeted Therapy?
Can c-Met Antibodies Become a New Hope for Tumor Targeted Therapy?
The c-Met receptor, a specific tyrosine kinase receptor for hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), has been a key target in cancer biology research since its discovery in 1985.
Cancerc-Met antibodycancer therapygrowth factor
Recent Advances
1. What Role Does the c-Met Receptor Play in Tumorigenesis and Development?
The c-Met receptor, a specific tyrosine kinase receptor for hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), has been a key target in cancer biology research since its discovery in 1985. This receptor consists of a 50kD β-chain and a 140kD α-chain linked by disulfide bonds. Its extracellular region contains SEMA, PSI, and four IPT domains, while the intracellular region contains a juxtamembrane domain and a tyrosine kinase domain. HGF binding induces receptor dimerization, triggering autophosphorylation at Y1234 and Y1235, thereby activating downstream signaling pathways.
c-Met expression is abnormally elevated in various epithelial-derived malignancies. Research data shows c-Met overexpression in 35-65% of breast cancers, 30-70% of gastric cancers, 25-60% of pancreatic cancers, 25-60% of hepatocellular carcinomas, 15-80% of renal cell carcinomas, and 35-70% of non-small cell lung cancers. This widespread and excessive expression makes c-Met an important target for cancer therapy. Beyond abnormal expression levels, genetic alterations such as c-Met gene amplification, mutations, fusions, and trans-activation are also significant factors driving tumorigenesis and progression.
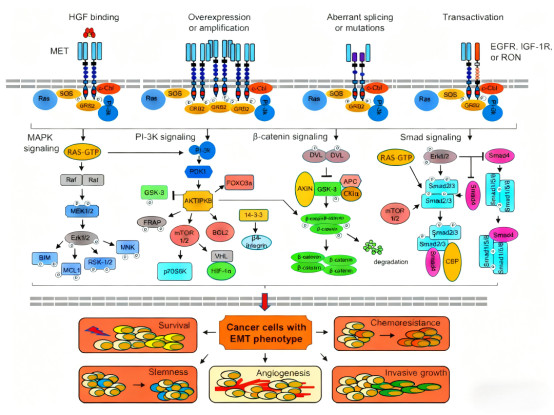
2. What Unique Advantages Do c-Met Antibody Drugs Offer?
Compared to traditional small molecule inhibitors, c-Met antibody drugs offer significant specificity advantages. Monoclonal antibodies can precisely recognize specific epitopes on the c-Met receptor, effectively inhibiting abnormal activation of downstream signaling pathways by blocking HGF binding. Furthermore, engineered antibodies can enhance anti-tumor effects through Antibody-Dependent Cell-mediated Cytotoxicity (ADCC).
Some c-Met antibody drugs utilize special Fc segment modification technologies, such as fully humanized design and site-specific acetylation modifications, which not only improve tissue penetration but also significantly enhance ADCC effects. These optimizations allow antibody drugs to maintain high specificity while possessing stronger immune-activating functions. Compared to traditional tyrosine kinase inhibitors, antibody drugs have a longer half-life and better tolerability, offering patients a more durable treatment option.
3. What Challenges Does c-Met Antibody Drug Development Face?
Although the prospects for c-Met antibody drug development are promising, several challenges remain. Firstly, c-Met is also expressed in normal tissues, so balancing efficacy and toxicity is a key consideration. Secondly, tumor cells may develop resistance through various mechanisms, including bypass signaling activation and epitope mutations. Clinical studies show that some c-Met monoclonal antibody drugs failed to meet endpoints in late-stage trials, indicating the need for more precise biomarkers to identify the patient population that will benefit.
Notably, the level of c-Met gene amplification is closely related to drug efficacy. Research data indicates that the response rate to targeted therapy increases with rising gene copy numbers. This dose-effect relationship underscores the importance of precision medicine in c-Met targeted therapy and suggests the need for a more comprehensive biomarker detection system to guide clinical medication.
4. What Breakthroughs Do Bispecific Antibodies and ADCs Bring?
Bispecific antibodies represent an important development direction in c-Met targeted therapy. These drugs can simultaneously recognize c-Met and other tumor-associated antigens, such as EGFR, exerting synergistic anti-tumor effects through dual blockade. Preclinical studies show that bispecific antibodies not only inhibit tumor growth more effectively but also reduce the emergence of resistance. Currently, several c-Met bispecific antibodies have entered clinical research stages globally, demonstrating promising application prospects.
Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADCs) link c-Met antibodies to highly potent cytotoxic agents via specific linkers, achieving a perfect combination of targeted delivery and precise killing. These drugs use the antibody's specificity to deliver the cytotoxic drug directly to c-Met overexpressing tumor cells, minimizing damage to normal tissues. ADCs utilizing site-specific conjugation technology allow precise control of the antibody-toxin ratio, further improving drug homogeneity and efficacy predictability.
5. How to Optimize the Clinical Application Strategy for c-Met Antibody Drugs?
To improve the clinical efficacy of c-Met antibody drugs, a comprehensive biomarker detection system needs to be established. Beyond traditional c-Met expression level detection, this should include multi-dimensional assessments such as gene amplification, mutation status, and proteomic characteristics. This information helps precisely identify patient populations likely to benefit from treatment, enabling personalized therapy.
Combination therapy strategies represent another important development direction. Combining c-Met antibodies with chemotherapy, immune checkpoint inhibitors, or other targeted drugs may produce synergistic effects and overcome the limitations of monotherapy. Particularly when combined with EGFR inhibitors, it can simultaneously block multiple signaling pathways, effectively preventing or delaying the onset of resistance. Furthermore, developing personalized dosing regimens based on the drug's mechanism of action and patient characteristics is also a key factor in improving treatment outcomes.
6. What is the Future Direction for c-Met Antibody Drugs?
With the deepening understanding of the c-Met signaling network, next-generation c-Met antibody drugs are evolving towards greater precision and efficiency. In drug design, novel antibody formats like bispecific antibodies and ADCs will continue to advance, improving treatment efficacy through multi-target synergy and precise drug delivery. In clinical development, biomarker-based patient stratification and adaptive clinical trial designs will become mainstream strategies.
From a broader perspective, the successful development of c-Met antibody drugs not only provides new treatment options for cancer patients but also offers valuable experience for the development of other tyrosine kinase receptor-targeted drugs. With continuous technological progress and accumulated clinical experience, c-Met antibody drugs are expected to play a more important role in the era of precision medicine, bringing new breakthroughs in cancer treatment.
7. Which Companies Provide c-Met Antibodies?
Hangzhou Start Biological Technology Co., Ltd. independently developed the "S-RMab® c-Met Recombinant Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody" (Product Name: S-RMab® c-Met Recombinant Rabbit mAb (SDT-009-7H0L0), Catalog Number: S0B2052). This is a high-performance antibody product characterized by high specificity, excellent sensitivity, and outstanding staining consistency. Developed using the proprietary S-RMab® recombinant rabbit monoclonal antibody technology platform and rigorously validated across multiple platforms including Immunohistochemistry (IHC), it holds key application value in areas such as tumor targeted therapy research, prognosis assessment, and invasion/metastasis mechanism studies.
Core Product Advantages:
High Specificity & Precise Membrane Localization: Precisely recognizes the c-Met (Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor) antigen, demonstrating exceptional cell membrane-specific staining in Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded (FFPE) samples with clear background and accurate localization, providing a reliable basis for precise interpretation.
Excellent Staining Stability & Batch Consistency: Under stringent quality control standards, the product exhibits superior staining stability and minimal inter-batch variation, ensuring comparability and reproducibility of results across different experiments, providing stable assurance for clinical research and drug development.
Suitable for Key Application Scenarios:
Related News
- Mouse T Cell Activation: A Systematic Guide to Developmental Differentiation and 3/12/2026
- Mouse T Cell Activation Kits: Enabling Efficient Immune Activation Through the C 3/11/2026
- Junshi Biosciences Announces NMPA Acceptance of New Drug Applications for Toripa 3/10/2026
- Rapport Therapeutics and Tenacia Biotechnology Announce Strategic Collaboration 3/10/2026
- Cas9 Antibodies: Ensuring Precision and Reproducibility in Gene Editing Research 3/10/2026
- Recombinant Rabbit Monoclonal Antibodies: Revolutionizing the Precision and Reli 3/9/2026
- Neural Research Antibodies: The Key to Unraveling the Mysteries of the Brain 3/8/2026
- The Key Role of CK-Pan Antibody in Cell Biology Research 3/7/2026
- Site-Selective Acetylation: Unlocking New Functional Horizons for Antibody Drugs 3/6/2026
- Lactylation Antibodies: Deciphering Novel Molecular Mechanisms of Metabolic Repr 3/5/2026


