Monolayer
Hydrophobic
Examples: C30, C18, C8, C4, Phenyl, Fluoro, etc.
Hydrophilic
Examples: Cyano, pyridine, amino, ethylene glycol, diol, imidazole, etc.
Ionic
Examples: Sulfonate (-SO3H, SCX), Carboxylate (-COOH, WCX), Quaternary ammonium (-NR3+, SAX), Tertiary amine (-NR2, WAX), etc.
Mixed Monolayer
Examples: Hydrophobic and Ionic (-SO3H, or -COOH, or -NR3+, or -NR2), etc.
Polymer Layer
Uniqueness
- Well controlled thickness: 1-100 nm
- Well controlled polarity from hydrophobic to hydrophilic
Examples: Polystyrene, a highly hydrophobic surface; Polyacrylamide, a highly hydrophilic surface
- Well controlled chemical properties from neutral to ionic
Examples: Polyethylene glycol, a neutral surface; Polymer functionalized with DEAE groups, a weak anionic surface
- Well controlled polymer chain density
- Mixed polymer layers;Examples: Hydrophobic and Ionic (-SO3H, or -COOH, or -NR3+, or -NR2), etc.
Substracts to Grow Organic Thin Films
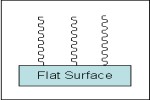
Flat Surface
Examples: Si wafers, Glass slides, TiO
2 plates, Au coated glass plates, Plastics sheets, Contact lens, etc.
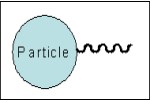
Particles
Examples: SiO2 micro-particles, PS/DVB particles, Au nanoparticles, Ag nanoparticles, TiO2 nano- and micro-particles, etc.
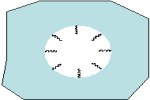
Porous materials
Examples: Porous SiO2 particles, Porous PS/DVB particles, Porous Polyacrylate particles, Polymer and Glass Membranes, etc.
Applications
- Anti-fouling;Protein resistance;Chromatographic separation;Micro-channel separation;Protein array;Membrane separation for biological molecules;Nanoparticle functionalization;Contact lens

