| Description | Detection Principle: This kit uses double antibody sandwich ELISA technology. The specific anti-human PD-L1 capture antibody was pre coated on a high affinity microplate. Add the standard, the sample to be tested and the biotin labeled detection antibody into the wells of the enzyme plate in turn, shake well and mix well, and then place it at room temperature for 2 hours of incubation process. The PD-L1 existing in the sample is combined with the solid-phase antibody and the detection antibody. After washing sufficiently to remove free and unbound components, streptavidin HRP (sa-hrp) labeled with horseradish peroxidase was added. After washing, signal enhancer was added for incubation. After washing to remove unbound material, sa-hrp was added again. After washing again, TMB chromogenic substrate was added and incubated at room temperature in the dark to develop color. The depth of color response is positively correlated with the concentration of PD-L1 in the sample. Add stop solution to stop the reaction, and use a microplate reader to measure the absorbance value at 450 nm detection wavelength (correction wavelength 570-630 nm). Detection Type: Double antibody sandwich method Form: Pre coated 96 well plate Test Sample Type: cell supernatant, serum, plasma Loading Amount: 100 μ L Kit Components: A copy of pre coated 96 well plate, standard, PD-L1 detection antibody, standard dilution, detection buffer, signal enhancer, signal enhancer dilution, TMB chromogenic substrate, washing solution, termination solution, sa-hrp, plate sealing membrane and instructions. Sensitivity: 0.49pg/ml Detection Range: 15.63-1000 pg/ml Recovery Range: 92-115% Storage Method: 2-8 ℃ Standard Curve: 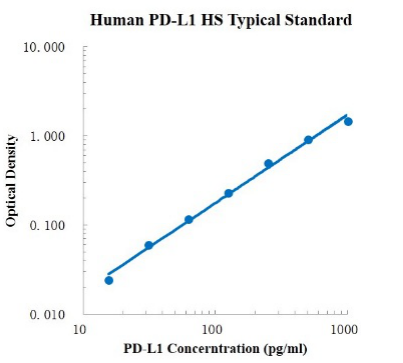
Background: B7 homolog 1 (B7-H1), also known as programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1), and differentiation group 274 (CD274), a type I transmembrane protein with a molecular weight of 40 kDa. B7-H1 may play an important role in specific events such as pregnancy, tissue transplantation, autoimmune diseases and immune system suppression of other diseases such as hepatitis. B7-H1 binds to its receptor to send inhibitory signals, which in turn reduces the proliferation of cd8+ T cells in lymph nodes. Upregulation of B7-H1 may cause tumor escape. Analysis of tumor specimens from 196 patients with renal cell carcinoma revealed that high expression of B7-H1 was associated with increased tumor invasion and increased risk of death (4.5-fold). In addition, B7-H1 can act as a positive costimulatory molecule for intracellular infection. In humans, the expression of B7-H1 is variable in children with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) |





