| Description | Testing Principle:
This kit uses double antibody sandwich ELISA.Specific anti-human IL-17A capture antibody is precoated on a high affinity conjugate plate. The standard substance, the sample to be tested and the detection antibody labeled with biotin were successively added into the HRP-plate well. After fully shaking and mixing, the IL-17A in the sample was placed at room temperature for a 2-hour incubation process. The IL-17A in the sample was combined with the solid phase antibody and the detection antibody. After washing thoroughly to remove free and unbound ingredients, horseradish peroxidase labeled streptavidin-HRP (SA-HRP) is added. After washing, signal enhancer was added for incubation. After washing and removing unbound substances, SA-HRP was added again. After washing again, TMB color substrate was added and incubated in dark at room temperature for color development. The depth of the color reaction was positively correlated with the concentration of IL-17A in the sample. The termination solution was added to terminate the reaction, and the absorbance value was measured at 450 nm detection wavelength (correction wavelength 570-630 nm) using a microplate analyzer. Detection type:Double sandwich enzyme immunoassay Form: pre-coated 96-well plate Sample type: Cell culture supernatant, Serum, Plasma Sample quantity:100 μl Kit composition:pre-coated 96-well plate,Standards,IL-12P70 Detection Antibody, Standard Diluent, Detection Buffer, Signal Enhancer, Signal Enhancer Diluent, TMB Color Substent, Washing Solution, Terminating Solution, SA-HRP, Sealing Plate Mask and Instructions Sensitivity:0.20 pg/mL Detection range:0.78-50 pg/mL Recovery rate:80-95% Storage:2-8℃ The standard curve: 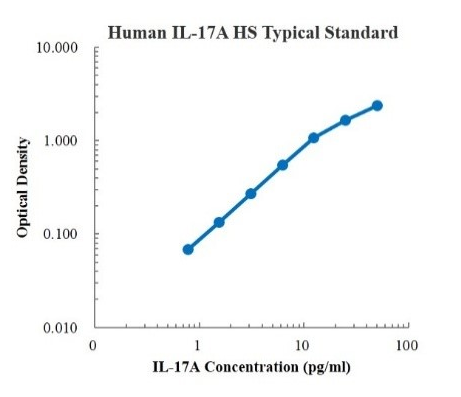 Background:
Interleukin 17A(IL-17 or IL-17A), a representative member of the IL-17 family of cytokines, is produced by helper T lymphocytes and can be induced by IL-23. IL-17 cytokines can effectively recruit monocytes and neutrophils to inflammatory sites by increasing the production of chemokines in tissues, thereby delaying the occurrence of inflammation. When an extracellular pathogen invades the immune system, IL-17, a pro-inflammatory cytokine, responds by destroying the pathogen's cells. IL-17 exerts synergistic effects with tumor necrosis factor and IL-1. The IL-17 family is associated with a number of immune/autoimmune-related diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, asthma, lupus, allograft rejection, anti-tumor immunity, psoriasis, multiple sclerosis. |





