- 8-OHDG ELISA Kit

- Product Detail
- Company Profile
- Precision
- Recovery
Product Specification
| Usage | I. Sample Collection, Preparation, and Storage 1. Serum: After placing whole blood samples at room temperature for 2 hours or at 4°C overnight, centrifuge at 1000×g for 20 minutes. Remove the supernatant for testing. Blood collection tubes should be disposable, pyrogen-free, and endotoxin-free. Store at -20°C or -80°C and avoid repeated freezing and thawing. 2. Plasma: Within 30 minutes of collection, centrifuge at 1000×g for 15 minutes at 2-8°C. Remove the supernatant for testing. EDTA-Na2 is recommended as the anticoagulant to avoid hemolysis or high-lipidemia samples. Store at -20°C or -80°C and avoid repeated freezing and thawing. 3. Tissue Homogenization: Take an appropriate amount of tissue and wash it in pre-chilled PBS (0.01M, pH 7.0-7.2) to remove blood (lysed red blood cells in the homogenate will affect the measurement results). After weighing, mince the tissue and mix it with the appropriate volume of PBS (generally a 1:9 mass-to-volume ratio; the specific volume can be adjusted according to experimental needs and recorded. It is recommended to add protease inhibitors to the PBS). Pour the mixture into a glass homogenizer and grind thoroughly on ice. To further lyse tissue cells, the homogenate can be sonicated or freeze-thawed repeatedly (keep the sonication in an ice bath and repeat the freeze-thaw cycle twice). Finally, centrifuge the homogenate at 5000×g for 5-10 minutes. Remove the supernatant for analysis. 4. Cell Culture Supernatant: Centrifuge the cell supernatant at 1000×g for 20 minutes to remove impurities and cell debris. Remove the supernatant for testing and store at -20°C or -80°C, but avoid repeated freezing and thawing. 5. Urine: Collect the first morning urine (midstream) or 24-hour urine collection. Centrifuge at 2000×g for 15 minutes, collect the supernatant, and store the sample at -20°C. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing. 6. Saliva: Collect the sample using a saliva collection tube, then centrifuge at 1000×g for 15 minutes at 2-8°C. Remove the supernatant for testing, or aliquot and store at -20°C. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing. 7. Other biological samples: Centrifuge at 1000×g for 20 minutes, collect the supernatant, and store at -20°C. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing.
Notes: 1. Samples should be clear and transparent, and suspended matter should be removed by centrifugation. Hemolysis of the sample will affect the results, so hemolyzed samples should not be used. 2. Samples can be stored at 4°C if tested within one week of collection. If testing cannot be performed promptly, aliquot the sample into single-use portions and freeze at -20°C (for testing within one month) or -80°C (for testing within three to six months). Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. Bring samples to room temperature before experimenting. 3. If the concentration of the test substance in your sample is higher than the highest concentration of the standard, dilute it appropriately based on the actual concentration (it is recommended to conduct a pilot experiment to determine the dilution factor). II.Preparation for the Test 1. Remove the test kit from the refrigerator 30 minutes in advance and equilibrate to room temperature. 2. Dilute 25 μg of concentrated wash buffer to 1 μg of working solution with double-distilled water. Return any unused solution to 4°C. 3. Standards: Add 1.0 mL of Universal Standard & Sample Diluent to the lyophilized standard. Tighten the cap and let stand for 10 minutes until fully dissolved. Then gently mix (concentration 100 ng/mL). Subsequently, perform serial dilutions to 100 ng/mL, 50 ng/mL, 25 ng/mL, 12.5 ng/mL, 6.25 ng/mL, 3.13 ng/mL, and 1.57 ng/mL. Use the standard diluent (0 ng/mL) as a blank well. Prepare the required amount of standard and set aside. It is recommended that the prepared standard be added to the sample within 15 minutes; it is not recommended to allow the sample to sit for extended periods. 4. Biotin Conjugate Working Solution (1x): Centrifuge before opening the bottle. Dilute with Biotin Conjugate Diluent immediately before use. Prepare the total volume required for each experiment (50 μL per well) based on the pre-calculated volume. Add 0.1-0.2 mL more, for example, 10 μL of biotin conjugate to 990 μL of biotin conjugate diluent. Mix gently and mix thoroughly. Prepare within one hour of use. 5. Streptomycin-Horseradish Peroxidase Conjugate Working Solution (1x): Centrifuge before opening the bottle. Dilute with enzyme conjugate diluent immediately before use. Prepare the pre-calculated total volume required for each experiment (100 μL per well). Prepare an extra 0.1-0.2 mL. For example, prepare 10 μL of enzyme conjugate to 990 μL of enzyme conjugate diluent. Mix gently. Prepare within one hour of use. 6. TMB Substrate - Pipette the required volume of solution. Do not pour any remaining solution back into the reagent bottle. Note: 1. Ensure all components of the kit are dissolved and mixed thoroughly before use. Discard any remaining standard after reconstitution. 2. Concentrated biotin conjugates and concentrated enzyme conjugates are relatively small and may disperse throughout the tube during transportation. Before use, centrifuge at 1000 × g for 1 minute to allow any liquid on the tube walls or cap to settle to the bottom. Mix the solution by carefully pipetting 4-5 times before use. Prepare the standard, biotin conjugate working solution, and enzyme conjugate working solution according to the required volume and use the corresponding diluents. Do not mix them. 3. Concentrated wash solution may crystallize after removal from the refrigerator. This is normal. Dissolve the crystals completely in a water bath or incubator before preparing the wash solution (do not heat above 40°C). The wash solution should be at room temperature before use. 4. Sample additions should be rapid, ideally within 10 minutes for each addition. To ensure experimental accuracy, replicate wells are recommended. When pipetting reagents, maintain a consistent order of addition from well to well. This will ensure consistent incubation times for all wells. 5. During the wash process, any remaining wash solution in the reaction wells should be patted dry on absorbent paper. Do not place filter paper directly into the reaction wells to absorb water. Before reading, be sure to remove any remaining liquid and fingerprints from the bottom of the wells to avoid affecting the microplate reader reading. 6. The color developer, TMB, should be protected from direct sunlight during storage and use. After adding the substrate, carefully observe the color change in the reaction wells. If a gradient is already evident, terminate the reaction early to avoid excessive color change that could affect the microplate reader reading. 7. All test tubes and reagents used in the experiment are disposable. Reuse is strictly prohibited, as this will affect the experimental results. 8. Please wear a lab coat and latex gloves for proper protection during the experiment, especially when testing blood or other body fluid samples. Please follow the national biological laboratory safety regulations. 9. Components from different batches of the kit should not be mixed (except for the wash solution and the reaction stop solution). 10. The enzyme labeling strips in the kit are removable. Please use them in batches according to experimental needs. III.Procedure 1. Before beginning the experiment, all reagents should be equilibrated to room temperature. Prepare all reagents in advance. When diluting reagents or samples, mix thoroughly, avoiding foaming as much as possible. If the sample concentration is too high, dilute with sample diluent to bring the sample within the detection range of the kit. 2. Sample Addition: Set up separate wells for standards and wells for the samples to be tested. Add 50 μL of the standard or sample to be tested, taking care not to create bubbles. Add the sample to the bottom of the ELISA plate well, minimizing contact with the well walls. Next, add 50 μL of biotin conjugate (1x) to each well, gently shake to mix. Cover the plate or cover with film, and incubate at 37°C for 1 hour. 3. To ensure the validity of the experimental results, use a fresh standard solution for each experiment. 4. After incubation for 1 hour, discard the liquid in the wells, spin dry, and wash the plate three times, adding 200 μL of washing solution (1 x) to each well, soaking for 1-2 minutes each time, and spin dry. 5. Then, add 100 μL of streptomycin-HRP (1 x) to each well, gently shake to mix, cover the plate or cover with film, and incubate at 37°C for 1 hour. 6. Discard the liquid in the wells, spin dry, and wash the plate five times, adding 200 μL of washing solution (1 x) to each well, soaking for 1-2 minutes each time, and spin dry. 7. Add 90 μL of TMB colorimetric reagent to each well and develop at 37°C in the dark for 15-20 minutes (shortening or extending the time may be appropriate based on the actual color development time, but should not exceed 30 minutes). 8. Add 50 μL of stop solution to each well in sequence to stop the reaction (the blue color will immediately turn yellow). The order of adding the stop solution should be as consistent as possible with the order of adding the substrate solution. To ensure accurate experimental results, add the stop solution as soon as possible after the substrate reaction time expires. 9. Measure the optical density (OD) of each well in sequence at 450 nm using a microplate reader. Measure within 5 minutes after adding the stop solution. 10. *Samples may require dilution. Please refer to the sample preparation section. Calculation of Results 1. The OD values of the competition standard and samples can be directly substituted into the calculation. If replicate wells are used, the average value should be used for calculation. 2. For ease of calculation, although concentration is the independent variable and OD value is the dependent variable, the OD value of the standard is used as the horizontal axis (X-axis) and the concentration of the standard is used as the vertical axis (Y-axis) in the plot. To ensure intuitiveness of the experimental results, the graphs provide raw data rather than logarithmic values. Due to differences in experimental operating conditions (such as operator, pipetting technique, plate washing technique, and temperature), the OD values of the standard curve may vary. The provided standard curve is for reference only; experimenters should establish a standard curve based on their own experiments. The sample concentration can be calculated from the OD value of the sample used on the standard curve and then multiplied by the dilution factor to obtain the actual sample concentration. It is recommended to use professional curve drawing software, such as Curve Expert.
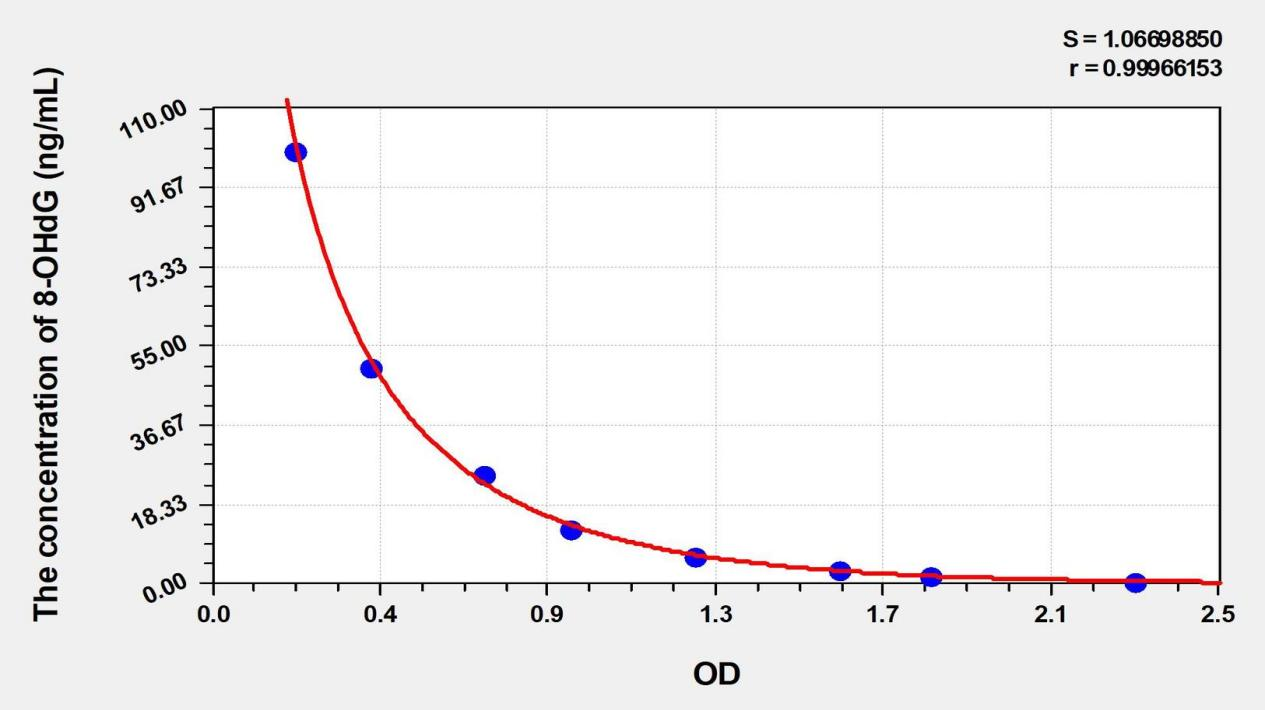 Note: This picture is for reference only Intra-assay precision (within-assay precision): CV% <8% Three samples of known concentration were tested 20 times on each ELISA plate to assess intra-assay precision. Inter-assay precision (between-assay precision): CV% <10% Three samples of known concentration were tested 40 times on each of three different ELISA plates to assess inter-assay precision. 8-OHDG at known concentrations was added to different samples for recovery experiments to obtain the recovery range and average recovery.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Species Reactivity | General | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Theory | This kit utilizes a competitive assay. Purified 8-OHDG is coated on a microplate to form a solid phase support. Samples or standards, followed by biotin-labeled antibodies, are sequentially added to the 8-OHDG-coated wells. Streptavidin-HRP is then added after the reaction. After thorough washing, the substrate TMB is used for color development. TMB is converted to blue by peroxidase and to yellow by acid. The intensity of the color is negatively correlated with the 8-OHDG content in the sample. The absorbance (OD) is measured at 450 nm using a microplate reader to calculate the sample concentration. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonym | 8OHdG; 7,8-Dihydro-8-Oxo-2'-Deoxyguanosine; 7,8-Dihydro-8-Oxodeoxyguanosine; 8-Hydroxy-2'-Deoxyguanosine; 8-Oxo-DG; 7,8-dihydrodeoxyguanosine | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Detection Type | It can detect recombinant or natural 8-OHDG and does not cross-react with other related proteins. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Composition |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General Notes |
1. If the entire kit is stored at -20°C, please place the kit at 4°C the night before the experiment. 2. Salt precipitation may occur when the concentrated wash solution is stored at low temperatures. When diluting, warm it in a water bath to help dissolve it. 3. A small amount of water-like substance may be present in the wells of a newly opened ELISA plate. This is normal and will not affect the experimental results. 4. This kit is for laboratory research and development use only and is not intended for use on humans or animals. 5. Reagents should be treated as hazardous substances and should be handled with care and disposed of properly. 6. Always wear gloves, lab coats, and protective glasses to avoid contact between skin and eyes with the stop solution and TMB. If contact occurs, rinse thoroughly with water. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Storage Temp. | Unopened test kit, stored at 4°C, has a shelf life of 6 months. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Test Range | 1.56-100 ng/mL; Sensitivity: 0.57 ng/mL |
-
AntBio is a biotechnology group company dedicated to serving life sciences, aiming to help scientists accelerate research and improve work efficiency. AntBio provides comprehensive and high-quality reagent tools for basic research, drug development, and diagnosis, including research grade antibodies, proteins, biochemical reagents, and assay kits. These research tools are widely used in different segments of life science research. The group company currently consists of three brands, Absin, Starter-Bio and UA-Bio.
| Request Information |
| Other Products |
| Related Products |
| Recently viewed products |
- SiteMap



