Detection Principle: This kit uses double antibody sandwich ELISA technology. Specific anti human crp Capture antibody was pre coated on a high affinity microplate. Add the standard, the sample to be tested and the biotin labeled detection antibody into the wells of the enzyme plate in turn, shake well and mix well, then place it at room temperature for 2 hours of incubation process, and the CRP in the sample; Bound to solid-phase antibody and detection antibody. After washing sufficiently to remove free and unbound components, streptavidin HRP (sa-hrp) labeled with horseradish peroxidase was added. After washing again, TMB chromogenic substrate was added and incubated at room temperature in the dark to develop color. The depth of color response is positively correlated with the concentration of CRP in the sample. Add stop solution to stop the reaction, and use a microplate reader to measure the absorbance value at 450 nm detection wavelength (correction wavelength 570-630 nm). Detection Type: Double antibody sandwich method Form: Pre coated 96 well plate Test Sample Type: cell supernatant, serum, plasma Loading Amount: 100 μ L Kit Components: A copy of pre coated 96 well plate, standard, human CRP detection antibody, detection buffer, TMB chromogenic substrate, washing solution, termination solution, sa-hrp, plate sealing membrane and instructions. Sensitivity: 0.44 pg/ml Detection Range: 62.5-4000pg/ml Recovery Range: 93-107% Storage Method: 2-8 ℃ Standard Curve: 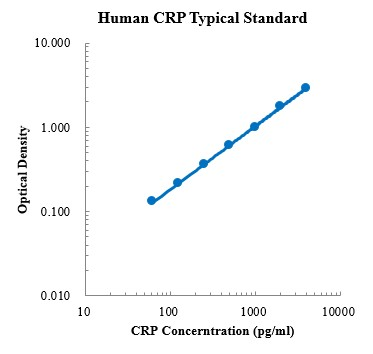
Background: C-reactive protein (CRP)It is a circular, pentameric protein found in plasma. The liver can synthesize CRP after responding to factors released by macrophages and adipocytes. CRP is a liver derived acute protein that increases after macrophages and T cells secrete interleukin-6. Its physiological role is to bind to lysophosphatidic choline on the surface of dead or dying cells (and some types of bacteria) to activate the complement system through C1q complex. It is not associated with C-peptide (insulin) or protein C (hemagglutination). CRP is usually used as an inflammatory marker. When the body is infected by inflammation, the CRP level will rise. Recent studies have shown that patients have a higher basal level of CRP, which is usually accompanied by a higher incidence of diabetes, hypertension and cardiovascular disease. | 




