| Usage | Experimental equipment required for the experiment:
1. Microplate reader (450nm)
2. High-precision pipette and gun tips: 0.5-10uL, 5-50uL, 20-200uL, 200-1000uL
3. 37℃ constant temperature box
4. Distilled water or deionized water
Sample processing and requirements:
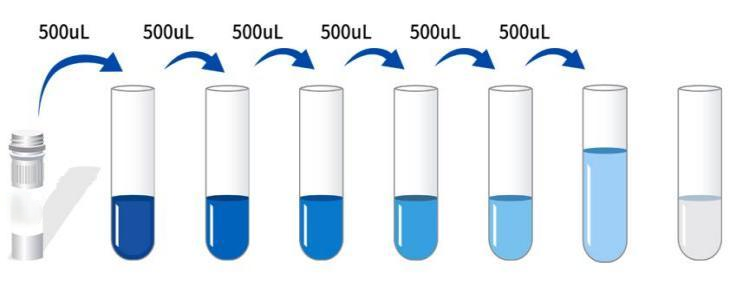
Serum: Place the whole blood sample collected in the serum separation tube at room temperature for 2 hours or at 4℃ overnight, then centrifuge at 1000×g for 20 minutes, and take the supernatant, or store the supernatant at -20℃ or -80℃, but avoid repeated freezing and thawing. Plasma: Collect the specimen using EDTA or heparin as an anticoagulant. Centrifuge the specimen at 1000 × g for 15 minutes at 2-8°C within 30 minutes of collection. The supernatant can be assayed or stored at -20°C or -80°C, but avoid repeated freezing and thawing. Tissue homogenization: Rinse the tissue with pre-chilled PBS (0.01M, pH 7.4) to remove residual blood (lysed red blood cells in the homogenate will affect the measurement results). Weigh the tissue and mince it. Add the minced tissue to the appropriate volume of PBS (generally a 1:9 weight-to-volume ratio, e.g., 1 g of tissue sample to 9 mL of PBS. The specific volume can be adjusted according to experimental needs and recorded. It is recommended to add protease inhibitors to the PBS) in a glass homogenizer and grind thoroughly on ice. To further lyse tissue cells, the homogenate can be sonicated or repeatedly frozen and thawed. Finally, centrifuge the homogenate at 5000 × g for 5-10 minutes, and the supernatant can be assayed. Other biological fluids: Centrifuge at 1000xg for 20 minutes, remove the supernatant, and test. Pre-test preparation: 1. Remove the test kit from the refrigerator 10 minutes in advance and equilibrate to room temperature. 2. Prepare the standard gradient working solution: Add 1 mL of universal diluent to the lyophilized standard, let it stand for 15 minutes to completely dissolve, then gently mix (concentration is 400 ng/mL). Then dilute to the following concentrations: 400 ng/mL, 200 ng/mL, 100 ng/mL, 50 ng/mL, 25 ng/mL, 12.5 ng/mL, 6.25 ng/mL, and 0 ng/mL. Serial dilution method: Take 7 EP tubes and add 500 μL of universal diluent to each tube. Pipette 500 μL of the 400 ng/mL standard working solution into the first EP tube and mix thoroughly to make a 200 ng/mL standard working solution. Repeat this procedure for subsequent tubes. The last tube serves directly as a blank well; there is no need to aspirate the liquid from the penultimate tube. See the figure below for details.
3. Preparation of Biotinylated Antibody Working Solution: 15 minutes before use, centrifuge the concentrated biotinylated antibody at 1000×g for 1 minute. Dilute the 100× concentrated biotinylated antibody to a 1× working concentration using universal diluent (e.g., 10µL concentrate + 990µL universal diluent). Prepare immediately before use. 4. Prepare the enzyme conjugate working solution: 15 minutes before use, centrifuge the 100× concentrated enzyme conjugate at 1000×g for 1 minute. Dilute the 100× concentrated HRP enzyme conjugate to a 1× working concentration with universal diluent (e.g., 10 μL of concentrate + 990 μL of universal diluent). Prepare immediately. 5. Prepare the 1× wash solution: Dispense 10 mL of 20× wash solution into 190 mL of distilled water (concentrated wash solution removed from the refrigerator may crystallize; this is normal. Allow to stand at room temperature until the crystals have completely dissolved before preparing). Procedure: 1. Remove the desired strips from the aluminum foil bag after equilibration at room temperature for 10 minutes. Seal the remaining strips in a ziplock bag and return to 4°C. 2. Sample addition: Add 100 μL of sample or standard of varying concentrations to the corresponding wells. Add 100 μL of universal diluent to the blank wells. Cover with a film and incubate at 37°C for 60 minutes. (Recommendation: Dilute the sample to be tested at least 1-fold with universal diluent before adding it to the ELISA plate. This will reduce the impact of matrix effects on the test results. The sample concentration should be multiplied by the corresponding dilution factor when calculating the final sample concentration. It is recommended to run replicates for all test samples and standards.) 3. Add Biotinylated Antibody: Remove the ELISA plate and discard the liquid without washing. Add 100 μL of Biotinylated Antibody Working Solution directly to each well. Cover with a film and incubate at 37°C for 60 minutes. 4. Wash: Discard the liquid and add 300 μL of 1x Wash Solution to each well. Let stand for 1 minute, shake off the wash solution, and pat dry on absorbent paper. Repeat this process three times (a plate washer can also be used). 5. Add Enzyme Conjugate Working Solution: Add 100 μL of Enzyme Conjugate Working Solution to each well. Cover with a film and incubate at 37°C for 30 minutes. 6. Washing: Discard the liquid and wash the plate five times as in step 4. 7. Adding substrate: Add 90 μL of substrate (TMB) to each well, cover with a sealing film, and incubate at 37°C in the dark for 15 minutes. 8. Adding stop solution: Remove the ELISA plate and add 50 μL of stop solution directly to each well. Immediately measure the OD value of each well at a wavelength of 450 nm. Calculating experimental results: 1. Calculate the average OD value of the standard and sample replicates and subtract the OD value of the blank well as a correction factor. Plot the standard curve of the four-parameter logistic function on double-logarithmic graph paper, with concentration as the horizontal axis and OD value as the vertical axis. 2. If the sample OD value is higher than the upper limit of the standard curve, dilute the sample appropriately and retest. Multiply the sample concentration by the corresponding dilution factor. |