|
Elucidating CD8α’s Core Mechanisms: Maintaining T Cell Homeostasis and Regulating Apoptosis
hits:35 Date:02/11/26
1. Concept
CD8α is a key co-receptor on T cell surfaces, with functions extending far beyond its traditional role in assisting MHC class I molecule recognition. As a transmembrane glycoprotein, it forms either homodimers (CD8αα) or heterodimers (CD8αβ) with CD8β, playing a pivotal role in T cell biology. Beyond enhancing TCR-MHC I binding affinity, CD8α is indispensable for maintaining peripheral T cell homeostasis—regulating the survival of naive and memory CD8⁺ T cell populations—and inhibiting abnormal apoptosis. Its multifunctional role positions it as a central regulator of adaptive immune system balance, with implications for immunity, inflammation, and disease pathogenesis.
2. Research Frontiers
2.1 CD8α’s Role in Maintaining T Cell Homeostasis
Studies using conditional knockout mouse models have clarified CD8α’s non-negotiable role in T cell homeostasis:
Population Reduction: CD8α deficiency leads to a significant decrease in peripheral naive and memory CD8⁺ T cell populations. Induced CD8α deletion reduces the survival rate of both subsets by 30–40%.
Peripheral Specificity: This reduction is not associated with thymic developmental abnormalities, indicating CD8α primarily regulates the survival and maintenance of mature peripheral T cells rather than T cell development.
2.2 Impact of CD8α Deficiency on T Cell Activation Status
CD8α deficiency induces a distinct phenotypic shift in T cells, reflecting disrupted homeostasis:
Activation Marker Dysregulation: In lymph nodes and spleen, CD8α-deficient T cells show significant upregulation of activation markers CD69 and FAS, alongside downregulation of homeostasis-related receptors CD127 (IL-7Rα) and CD122 (IL-2Rβ).
TCR-Independent Mechanism: CD5 expression is downregulated in these cells, suggesting the observed homeostasis disruption occurs independently of TCR signaling pathways.
2.3 Specific Mechanisms of CD8α-Mediated T Cell Apoptosis Regulation
In vitro experiments confirm CD8α’s direct role in modulating T cell sensitivity to apoptotic signals:
Enhanced Apoptotic Susceptibility: CD8α-deficient naive and memory T cells exhibit higher levels of programmed cell death when induced by anti-FAS antibodies.
Molecular Regulation: CD8α maintains long-term T cell survival by modulating death receptor signaling pathways (e.g., FAS-FASL) and regulating the expression of anti-apoptotic proteins—preventing uncontrolled cell loss.
2.4 CD8α-PILRα Interaction in Maintaining T Cell Quiescence
A key discovery in CD8α biology is its specific interaction with PILRα (Paired Immunoglobulin-Like Type 2 Receptor α), which underpins T cell quiescence:
Quiescence Maintenance: Under physiological conditions, the CD8α-PILRα complex suppresses aberrant activation signals, preserving the T cell’s quiescent phenotype.
Dysregulation in Deficiency: CD8α deletion abrogates this inhibitory effect, leading to spontaneous T cell activation and subsequent apoptosis—providing a novel theoretical framework for understanding T cell homeostasis.
2.5 Impact of CD8α Deficiency on Immune Protection
CD8α’s role in maintaining T cell populations and function is critical for adaptive immune defense:
Increased Pathogen Susceptibility: CD8α-deficient mice are more vulnerable to pathogen infections, directly demonstrating CD8α’s importance in sustaining immune protection.
Multifaceted Immunodeficiency: This vulnerability stems from both reduced CD8⁺ T cell numbers and functional abnormalities in surviving T cells, compromising cytotoxic responses and immune memory.
2.6 Application Value and Development Prospects of CD8α Antibodies
CD8α-specific antibodies are indispensable tools for immunology research and translational applications:
Research Utility: Antibody-mediated detection and functional intervention enable precise analysis of CD8α expression and function across T cell subsets.
Technological Synergy: Combined with single-cell sequencing and multi-omics analysis, CD8α antibodies facilitate refined immune cell typing and functional characterization.
Therapeutic Potential: Immune therapy strategies targeting CD8α-regulated mechanisms—such as enhancing T cell survival in cancer or suppressing abnormal activation in autoimmunity—are emerging as promising research directions.
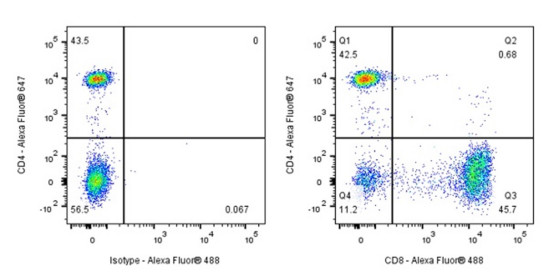
3. Research Significance
CD8α’s role as a central regulator of T cell homeostasis and apoptosis addresses a critical gap in understanding immune system regulation. By maintaining T cell quiescence and inhibiting excessive apoptosis, CD8α ensures the adaptive immune system retains sufficient functional T cells to respond to pathogens while avoiding pathological activation. Insights into its mechanisms—including interactions with PILRα and regulation of death receptor pathways—expand our knowledge of immune balance and provide novel therapeutic targets for immune-related diseases (e.g., cancer, autoimmunity, immunodeficiency). Additionally, CD8α’s utility as a cytotoxic T cell marker makes it invaluable for tumor immunology research and immunotherapy efficacy evaluation, bridging basic science and clinical application.
4. Related Mechanisms, Research Methods, and Product Applications
4.1 Mechanisms
CD8α regulates T cell biology through two core pathways:
Homeostasis Maintenance: The CD8α-PILRα interaction suppresses spontaneous T cell activation, preserving quiescence and preventing premature apoptosis.
Apoptosis Regulation: CD8α modulates death receptor signaling (e.g., FAS-FASL) and anti-apoptotic protein expression, reducing T cell susceptibility to apoptotic signals and ensuring long-term survival.
4.2 Research Methods
Key research methods for studying CD8α include:
Genetic Models: Conditional knockout mice to assess CD8α’s in vivo function in T cell homeostasis and survival.
Phenotypic Analysis: Flow cytometry to quantify CD8α expression and detect changes in activation (CD69, FAS) and homeostasis (CD127, CD122) markers.
Functional Assays: In vitro apoptosis assays (e.g., anti-FAS antibody induction) to evaluate CD8α’s role in regulating cell death.
Imaging and Detection: Immunohistochemistry (IHC) to localize CD8α⁺ T cells in tissues, and co-immunoprecipitation to validate interactions (e.g., CD8α-PILRα).
4.3 Product Applications
ANT BIO PTE. LTD.’s CD8α antibodies, led by the STARTER brand’s "S-RMab® CD8α Mouse Monoclonal Antibody" (Catalog No.: S0B2307), are high-performance tools for immunology research and clinical translation:
Cytotoxic T Cell Identification & Quantification: Enables precise detection and infiltration level analysis of CD8⁺ T cells in tumor tissues, infection sites, and autoimmune lesions.
Tumor Immune Microenvironment Evaluation: Serves as a key indicator for assessing the proportion and distribution of CD8⁺ T cells in tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs), supporting prognosis and immunotherapy efficacy analysis.
Immunotherapy Efficacy Prediction & Monitoring: Facilitates patient screening before immune checkpoint inhibitor (e.g., anti-PD-1/PD-L1) treatment and dynamic monitoring of immune microenvironment changes post-treatment.
Transplant Immunology Research: Detects and quantifies CD8⁺ T cell infiltration during graft rejection, aiding in rejection diagnosis and management.
The S0B2307 antibody, developed using ANT BIO PTE. LTD.’s proprietary S-RMab® mouse monoclonal platform and validated for IHC and flow cytometry, offers exceptional advantages: high specificity with clear membrane localization (ensuring reliable CD8⁺ T cell identification in FFPE samples and cell preparations) and superior staining/labeling stability with minimal batch variation—critical for consistent results in clinical research and translational medicine.
5. Brand Mission
ANT BIO PTE. LTD. is dedicated to empowering the global life science community with high-quality, innovative biological reagents and solutions. Leveraging advanced development platforms—including recombinant rabbit monoclonal antibody, recombinant mouse monoclonal antibody, rapid monoclonal antibody, and multi-system recombinant protein expression platforms (E.coli, CHO, HEK293, Insect Cells)—and adhering to rigorous international certifications (EU 98/79/EC, ISO9001, ISO13485), we strive to deliver reliable, performance-proven tools that accelerate scientific breakthroughs in immunology, oncology, and translational medicine. Our commitment to quality and innovation aims to support researchers and clinicians in advancing human health through cutting-edge life science research and precision therapy.
6. Related Product List
| Catalog No. |
Product Name |
Host |
| S0B2307 |
S-RMab® CD8α Mouse mAb (SDT-1036-34) |
Mouse |
| S0B1141 |
Invivo anti-Mouse CD8α Recombinant mAb |
Rat |
| S0B1662 |
Alexa Fluor® 700 Rat Anti-Mouse CD8α Antibody (S-353-45) |
Rat |
| S0B1164 |
CD8α Recombinant Mouse mAb (S-1036-21) |
Mouse |
| S0B1804 |
FITC Rat Anti-Mouse CD8α Antibody (S-R540) |
Rat |
7. AI Disclaimer
This article is AI-compiled and interpreted based on the original work. All intellectual property (e.g., images, data) of the original publication shall belong to the journal and the research team. For any infringement, please contact us promptly and we will take immediate action.
ANT BIO PTE. LTD. – Empowering Scientific Breakthroughs
At ANTBIO, we are committed to advancing life science research through high-quality, reliable reagents and comprehensive solutions. Our specialized sub-brands (Absin, Starter, UA) cover a full spectrum of research needs, from general reagents and kits to antibodies and recombinant proteins. With a focus on innovation, quality, and customer-centricity, we strive to be your trusted partner in unlocking scientific mysteries and driving medical progress. Explore our product portfolio today and elevate your research to new heights.
|