|
CD79B Antibodies: Emerging as a Precise Target for B Cell-Related Disease Therapy
hits:31 Date:02/10/26
1. Concept
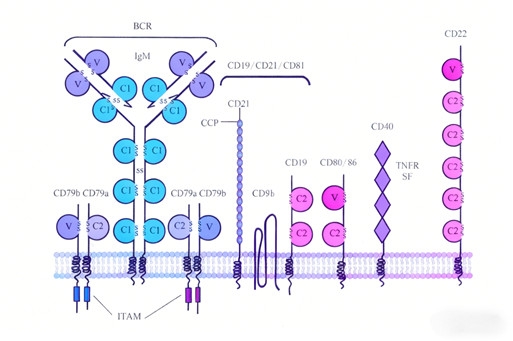
CD79B is a core component of the B cell receptor (BCR) complex, forming a defining surface marker of B cells alongside CD79A. This transmembrane protein non-covalently associates with membrane-bound immunoglobulins to assemble a functional BCR complex, which transmits antigen recognition signals into the cell. Expressed across all stages of B cell development except terminally differentiated plasma cells, CD79B is indispensable for B cell activation, proliferation, and functional execution. Its B cell-specific expression pattern and central role in BCR signaling position it as a highly promising target for the treatment of B cell-related diseases, including hematological malignancies and autoimmune disorders.
2. Research Frontiers
2.1 Core Role of CD79B in B Cell Biology
CD79B’s function is central to B cell physiology:
Signal Transduction: As part of the BCR complex, CD79B contains immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs (ITAMs) in its cytoplasmic domain. Upon antigen binding, these ITAMs are phosphorylated, initiating downstream signaling cascades (e.g., Syk, PI3K-AKT) that drive B cell activation and differentiation.
Developmental Regulation: CD79B is essential for B cell maturation—its absence leads to defective B cell development and impaired humoral immunity.
Functional Specificity: Restricted expression to B cells (excluding plasma cells) ensures that targeting CD79B selectively modulates B cell function without affecting other immune cell lineages.
2.2 Molecular Mechanisms and Design Principles of CD79B-Targeted Therapy
CD79B-targeted therapies leverage its unique biological properties for precise intervention:
Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADCs): ADCs consist of a CD79B-specific antibody conjugated to a cytotoxic payload. The antibody binds CD79B on B cell surfaces, and receptor-mediated endocytosis delivers the payload into target cells, inducing selective cell death.
Bispecific Antibodies: These molecules feature one arm targeting CD79B (to engage B cells) and another arm binding immune effector cells (e.g., T cells, NK cells) or signaling regulators. This design enables more complex functions, such as redirecting effector cells to eliminate B cells or modulating B cell signaling.
Biparatopic Antibodies: Engineered to bind two distinct epitopes on CD79B, these antibodies enhance binding affinity and specificity, improving therapeutic efficacy while reducing off-target effects.
2.3 Clinical Breakthroughs of CD79B-Targeted Drugs in Hematological Tumors
CD79B-targeted therapies have transformed the treatment landscape for B cell hematological malignancies:
Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL): Clinical trial data show that combination regimens containing CD79B-targeted ADCs significantly improve progression-free survival (PFS) in patients with relapsed/refractory DLBCL. Compared to traditional treatments, these combinations reduce the risk of disease progression by approximately 27%.
Broad Applicability: CD79B-targeted drugs are also being evaluated in other B cell malignancies, including follicular lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), and mantle cell lymphoma, with promising preliminary results.
Unmet Need Address: These therapies provide new options for patients who have failed conventional chemotherapy or other targeted agents, addressing a critical unmet need in hematological oncology.
2.4 Application Prospects in Autoimmune Diseases
Beyond cancer, CD79B-targeted strategies hold great potential for autoimmune diseases:
Precision Modulation: Unlike therapies that deplete all B cells, CD79B-targeted drugs modulate B cell function specifically—suppressing pathological antibody production and pro-inflammatory signaling without causing widespread B cell depletion.
Target Diseases: Early clinical studies indicate efficacy in conditions such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA), where pathogenic B cells drive disease progression.
Safety Profile: These agents demonstrate good tolerability, with fewer off-target effects compared to non-specific B cell-depleting therapies, making them suitable for long-term management of chronic autoimmune diseases.
2.5 Technological Trends and Innovative Directions in CD79B Drug Development
CD79B-targeted drug development is evolving toward diversified and refined approaches:
Novel Molecular Formats: Beyond ADCs, bispecific antibodies, biparatopic antibodies, and antibody-fusion proteins are emerging to enhance targeting precision and therapeutic versatility.
Combination Targeting: Strategies combining CD79B with other B cell surface markers (e.g., CD20, CD38) or immune checkpoints aim to achieve synergistic effects, improving efficacy in complex diseases.
Payload Optimization: New cytotoxic payloads with improved potency, reduced toxicity, or novel mechanisms of action are being integrated into CD79B-targeted ADCs to enhance therapeutic index.
2.6 Future Directions and Challenges for CD79B-Targeted Therapy
Despite significant progress, CD79B-targeted therapy faces key opportunities and challenges:
Indication Expansion: Validating efficacy in a broader range of B cell-related diseases—from rare hematological malignancies to autoimmune disorders—requires additional clinical research.
Technical Optimization: Improving targeting efficiency, minimizing off-target toxicity, and overcoming drug resistance (e.g., via epitope engineering or combination therapies) are critical for long-term success.
Combination Regimens: Exploring synergies with immunotherapies (e.g., immune checkpoint inhibitors, CAR-T cells), chemotherapy, or targeted agents to maximize treatment outcomes.
Biomarker Development: Identifying predictive biomarkers to select patients most likely to respond to CD79B-targeted therapy, enabling personalized treatment approaches.
3. Research Significance
CD79B-targeted therapy represents a major advancement in precision immunotherapy, addressing the unmet need for selective B cell modulation in disease. By targeting a core component of the BCR complex, these therapies achieve precise control of B cell function—eliminating malignant B cells in cancer and suppressing pathogenic B cells in autoimmune diseases while preserving normal immune function. This specificity reduces treatment-related toxicity and improves patient quality of life. Additionally, CD79B’s role as a B cell-specific marker makes it invaluable for diagnostic applications (e.g., lymphoma subtyping, minimal residual disease detection), bridging basic research, clinical diagnosis, and therapy. Insights into CD79B’s signaling mechanisms also advance our understanding of B cell biology, informing the development of therapies for other immune-related conditions.
4. Related Mechanisms, Research Methods, and Product Applications
4.1 Mechanisms
CD79B-targeted therapies act through two primary mechanisms:
Direct Cytotoxicity: ADCs deliver cytotoxic payloads into CD79B-positive B cells, inducing apoptosis or necrosis.
Functional Modulation: Bispecific antibodies or non-cytotoxic CD79B antibodies modulate BCR signaling, suppressing pathological antibody production and pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion without killing B cells—ideal for autoimmune diseases.
4.2 Research Methods
Key research methods for studying CD79B include:
Expression Analysis: Immunohistochemistry (IHC), flow cytometry, and Western blotting to detect CD79B expression in B cells and tissues.
Functional Assays: B cell activation assays, antibody secretion assays, and signaling pathway analysis (e.g., phospho-flow cytometry) to evaluate the effects of CD79B-targeted agents.
Preclinical and Clinical Evaluation: Xenograft models, patient-derived organoids, and clinical trials to assess efficacy, safety, and pharmacokinetics of CD79B-targeted drugs.
Minimal Residual Disease (MRD) Detection: Flow cytometry or PCR-based assays using CD79B as a marker to monitor residual B cell malignancies post-treatment.
4.3 Product Applications
ANT BIO PTE. LTD.’s CD79B antibodies, highlighted by the STARTER brand’s "S-RMab® CD79B Recombinant Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody" (Catalog No.: S0B2347), are critical tools for B cell research and clinical diagnostics:
B-Cell Lymphoma Diagnosis and Classification: Enables precise diagnosis and differential diagnosis of DLBCL, follicular lymphoma, CLL, and other B cell malignancies.
B-Cell Development and Differentiation Research: Facilitates studies on B cell maturation in bone marrow and differentiation in peripheral lymphoid tissues.
Immune Microenvironment Analysis: Evaluates B cell infiltration in tumor and autoimmune disease tissues, supporting research on disease pathogenesis and treatment response.
Minimal Residual Disease Detection: Serves as a specific B cell marker for MRD monitoring post-treatment, enabling early detection of relapse.
The S0B2347 antibody, developed using ANT BIO PTE. LTD.’s proprietary S-RMab® recombinant rabbit monoclonal platform and validated for IHC, offers exceptional advantages: high specificity with clear membrane localization (ensuring reliable B cell identification in FFPE samples) and superior staining stability with minimal batch variation—critical for consistent results in clinical diagnostics and translational research.
5. Brand Mission
ANT BIO PTE. LTD. is dedicated to empowering the global life science community with high-quality, innovative biological reagents and solutions. Leveraging advanced development platforms—including recombinant rabbit monoclonal antibody, recombinant mouse monoclonal antibody, rapid monoclonal antibody, and multi-system recombinant protein expression platforms (E.coli, CHO, HEK293, Insect Cells)—and adhering to rigorous international certifications (EU 98/79/EC, ISO9001, ISO13485), we strive to deliver reliable, performance-proven tools that accelerate scientific breakthroughs in hematology, oncology, and immunology. Our commitment to quality and innovation aims to support researchers and clinicians in advancing human health through precise diagnosis and cutting-edge life science research.
6. Related Product List
| Catalog No. |
Product Name |
Host |
| S0B2347 |
S-RMab® CD79B Recombinant Rabbit mAb
(SDT-R513) |
Rabbit |
| S0B2347P |
S-RMab® CD79B Recombinant Rabbit mAb, PBS Only
(SDT-R513) |
Rabbit |
| S0B2021 |
CD79B Recombinant Rabbit mAb
(SDT-043-9) |
Rabbit |
| S0B2021P |
CD79B Recombinant Rabbit mAb, PBS Only
(SDT-043-9) |
Rabbit |
| UA010276 |
CD79B His Tag Protein, Human |
Human |
7. AI Disclaimer
This article is AI-compiled and interpreted based on the original work. All intellectual property (e.g., images, data) of the original publication shall belong to the journal and the research team. For any infringement, please contact us promptly and we will take immediate action.
ANT BIO PTE. LTD. – Empowering Scientific Breakthroughs
At ANTBIO, we are committed to advancing life science research through high-quality, reliable reagents and comprehensive solutions. Our specialized sub-brands (Absin, Starter, UA) cover a full spectrum of research needs, from general reagents and kits to antibodies and recombinant proteins. With a focus on innovation, quality, and customer-centricity, we strive to be your trusted partner in unlocking scientific mysteries and driving medical progress. Explore our product portfolio today and elevate your research to new heights.
|