|
Absin Human HCC Organoid Kit Facilitates Solving Hepatocellular Carcinoma TKI Resistance
hits:35 Date:10/27/25
Recently, the international top journal Nature Cancer (IF 28.5) published an online breakthrough study on the resistance mechanism of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) targeted therapy, revealing that RIOK1 mediates stress granule formation via phase separation, inhibits PTEN translation, and activates the pentose phosphate pathway, ultimately leading to tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) resistance in HCC cells. Notably, the critical clinical translation verification experiment in this study—the establishment of the patient-derived HCC organoid (PDO) model—was fully completed using the Absin Human HCC Organoid Kit (abs9444), providing core technical support for the clinical relevance of the research conclusions.
Article Title: RIOK1 phase separation restricts PTEN translation via stress granules activating tumor growth in hepatocellular carcinoma
Published in: Nature Cancer (IF 28.5)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s43018-025-00984-5
Core Reagent: Human HCC Organoid Culture Kit (abs9444)
1. Research Background: Urgent Need to Address TKI Resistance in HCC
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. Multitarget TKIs (e.g., sorafenib, donafenib) are first-line treatment options for advanced HCC. However, due to adaptive changes in cells triggered by tumor microenvironment stress (such as nutrient deficiency, hypoxia), TKI resistance severely limits clinical efficacy. Previous studies have shown that stress granules (SGs, formed by liquid-liquid phase separation, LLPS) are associated with drug resistance, but the specific mechanism in HCC remains unclear—which is the core scientific question this study aims to solve.
2. Core Finding: The RIOK1-Stress Granule-PTEN Axis is Key to TKI Resistance
Through multi-platform screening, the research team found that the atypical kinase RIOK1 is highly expressed in HCC and associated with poor prognosis. After being stress-activated under the regulation of NRF2, RIOK1 recruits IGF2BP1 and G3BP1 to form stress granules via LLPS, sequestering PTEN mRNA and inhibiting its translation. Decreased PTEN expression activates the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP), enhancing the stress tolerance and TKI resistance of HCC cells; while the small-molecule drug chidamide can target and degrade RIOK1, synergizing with TKIs to inhibit tumor growth (Figure 1).
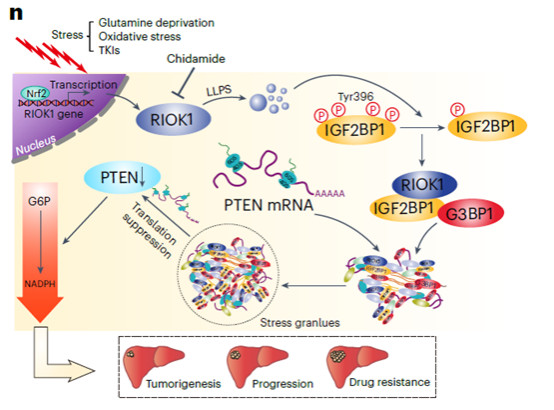
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of the core research mechanism: Molecular pathway of RIOK1-mediated TKI resistance
3. Absin Human HCC Organoid Kit: A "Key Tool" for Clinical Translation Verification
To verify whether the synergistic therapeutic effect of chidamide and TKI (donafenib) is clinically relevant, the research team needed to establish an in vitro model that retains the heterogeneity of patient tumors—patient-derived HCC organoids (PDOs). The establishment of this model relies on the Absin Human HCC Organoid Kit (abs9444), whose core roles are reflected in the following three aspects:
3.1 Efficient Establishment of Clinically Relevant PDO Models
The research team used the Absin Kit to culture organoids from tumor tissues of HCC patients (Patient 2, Patient 7) who underwent surgical treatment:
* Procedure: Tumor tissues were cut into 1 mm³ pieces, subjected to enzymatic digestion, filtration, and centrifugation. The cells were then resuspended in the special medium provided in the kit, mixed with Matrigel for seeding. The kit-matched medium was replaced every 2-3 days, and passaging was performed every 5-7 days (passaged 3 times before use in experiments).
* Advantages: The Absin Kit contains optimized basement membrane components, growth factor cocktails, and anti-contamination reagents, which can efficiently maintain the in vivo morphology, heterogeneity, and drug response characteristics of HCC cells, solving the problem that traditional cell lines "deviate from clinical reality".
3.2 Verification of Clinical Inhibitory Effect of Combined Drug Therapy
Using the PDO model established with the Absin Kit, the research tested the synergistic effect of "chidamide + donafenib":
* Results: Compared with the single-drug treatment groups, the combined treatment group significantly reduced PDO volume (Figure 2o), and showed consistent growth inhibition effects on PDOs derived from different patients (Figure 2p), demonstrating the broad clinical potential of this combined regimen.
* Corresponding Key Images: Figure 2o shows microscopic images of PDOs in the DMSO, donafenib, chidamide, and combined treatment groups (obvious shrinkage of organoids in the combined treatment group is visible); Figure 2p shows statistical data of PDO area changes (the area of the combined treatment group was significantly lower than that of the single-drug groups, P<0.0001).
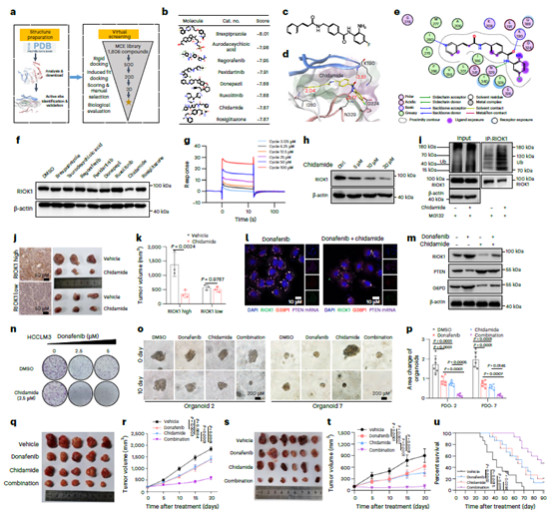
Figure 2 Inhibitory effect of combined drug therapy on PDOs: Left = morphological changes; Right = volume quantitative statistics
3.3 Supporting the "Basic Mechanism-Clinical Translation" Loop
To further confirm the reliability of the organoid model, the research also performed HE staining verification on PDOs established with the Absin Kit, proving that the cultured organoids retained the histological characteristics of the primary tumor. Meanwhile, combined with in vivo experiments using the mouse PDX model (patient-derived xenograft), a complete evidence chain of "cell experiment-PDO verification-animal verification" was formed. The PDO model established with the Absin Kit serves as the "bridge" connecting basic mechanisms and clinical applications.
4. Advantages of the Absin Kit: Why It Became the First Choice of the Research Team?
The research team chose the Absin Human HCC Organoid Kit mainly due to its three core advantages, which match the needs of clinical translation research:
(1) High Success Rate and Stability: The kit is optimized for the characteristics of HCC cells, enabling successful PDO establishment from more than 80% of patient tumor tissues. It can maintain stable passaging for more than 10 generations while preserving tumor heterogeneity.
(2) Strong Clinical Relevance: The cultured PDOs can simulate the differences in patient tumor responses to drugs (e.g., in the original article, PDOs from different patients showed consistent sensitivity to the combined treatment, but with differences in absolute inhibition rates), providing a reliable model for personalized therapy research.
(3) Operational Convenience: The kit provides a complete culture system (including special medium, Matrigel, digestive solution) and standard operating guidelines, eliminating the need for researchers to explore formulas independently and significantly shortening the model establishment cycle.
5. Conclusion: Absin Empowers HCC Research from "Basic" to "Clinical"
This Nature Cancer study not only reveals a new mechanism of TKI resistance in HCC and provides a theoretical basis for the development of combined therapy of "RIOK1 inhibitor + TKI", but also demonstrates the irreplaceable role of patient-derived organoids (PDOs) in clinical translation research. As the core tool for PDO model establishment in this study, the reliability and clinical relevance of the Absin Human HCC Organoid Kit (abs9444) have been verified by top scientific achievements.
In the future, Absin will continue to focus on research tools in fields such as tumor organoids and cell biology, providing "one-stop support from reagents to solutions" for more cancer mechanism research, drug screening, and personalized therapy research. We will help researchers accelerate the resolution of key problems and promote the development of precision medicine.
Products Used in the Article
| Catalog No. |
Name |
Specification |
| abs9444 |
Human HCC Organoid Culture Kit |
1 kit |
More Organoid Culture Kits
| Category |
Catalog No. |
Product Name |
Specification |
| Liver |
abs9544 |
Human Normal Liver Organoid Culture Kit |
1 kit |
| |
abs9786 |
Human Hepatobiliary Duct Carcinoma Organoid Culture Kit |
1 kit |
| |
abs9516 |
Mouse Normal Liver Organoid Culture Kit |
1 kit |
| |
abs9552 |
Mouse HCC Organoid Culture Kit |
1 kit |
| |
abs9779 |
Pig Normal Liver Organoid Medium Kit |
1 kit |
| Intestine |
abs9545 |
Human Normal Intestine Organoid Culture Kit |
1 kit |
| |
abs9445 |
Human Intestinal Cancer Organoid Culture Kit |
1 kit |
| |
abs9514 |
Mouse Normal Small Intestine Organoid Culture Kit |
1 kit |
| |
abs9985 |
Mouse Normal Colon Organoid Culture Kit |
1 kit |
| |
abs9548 |
Mouse Intestinal Cancer Organoid Culture Kit |
1 kit |
| |
abs9757 |
Balb/C Mouse Normal Small Intestine Organoid Culture Kit |
1 kit |
| |
abs9758 |
Balb/C Mouse Normal Colon Organoid Culture Kit |
1 kit |
| |
abs9762 |
Rat Normal Small Intestine Organoid Culture Kit |
1 kit |
| |
abs9763 |
Rat Normal Colon Organoid Culture Kit |
1 kit |
| |
abs9760 |
Rat Fetal Normal Small Intestine Organoid Culture Kit |
1 kit |
| |
abs9761 |
Rat Fetal Normal Colon Organoid Culture Kit |
1 kit |
| |
abs9889 |
Pig Normal Intestine Organoid Culture Kit |
1 kit |
| Intestine |
abs9911 |
Bovine Normal Intestine Organoid Culture Kit |
1 kit |
| |
abs90066 |
Chicken Small Intestine Organoid Medium Kit |
1 kit |
|