Home > News > A Guide to Anti-Idiotypic Antibodies: From Definition, Classification to Customized Solutions
A Guide to Anti-Idiotypic Antibodies: From Definition, Classification to Customized Solutions
- I. Definition of Anti-Idiotypic Antibodies
The idiotype refers to the totality of unique antigenic determinants present on an antibody molecule. A single antibody molecule can possess multiple idiotypic determinants, reflecting the diversity of antibody molecules. These antigenic determinants on the antibody molecule are called idiotopes, which can be located in the hypervariable regions or the framework regions of the antibody's variable (V) domain. Idiotypic determinants can induce the production of corresponding antibodies in heterologous, allogeneic, and even autologous systems. These induced antibodies are called anti-idiotypic antibodies (AId or Ab2). Idiotypes and anti-idiotypic antibodies can form a complex network, playing a significant role in immune regulation.
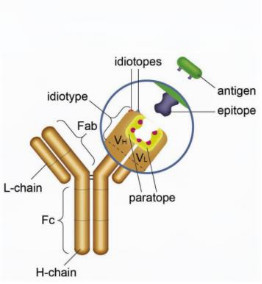
II. Classification of Anti-Idiotypic Antibodies
Antigen-Blocking (Neutralizing) Anti-Idiotypic Antibodies: These recognize idiotopes that overlap with the antigen epitope of the therapeutic antibody. They compete with the antigen for binding to the therapeutic antibody, and therefore can only detect the antigen-free (unbound) form of the therapeutic antibody.
Non-Blocking (Non-Neutralizing) Anti-Idiotypic Antibodies: These recognize idiotopes that do not overlap with the antigen epitope of the therapeutic antibody. They can bind to the therapeutic antibody simultaneously with the antigen without mutual interference. Lacking paratope specificity, they can detect the total amount of the therapeutic antibody, including both the free form and the antigen-bound form.
Complex-Specific (Drug-Target Complex) Anti-Idiotypic Antibodies: These specifically recognize the complex formed between the "therapeutic antibody and its target antigen" and do not bind to the antibody or antigen alone. Therefore, they can only detect the target-bound form of the therapeutic antibody.
III. Biological Functions of Anti-Idiotypic Antibodies
(1) Immune Suppression and Immune Activation
Regarding immune suppression, Ab2 can inhibit the function of Ab1. This inhibition is achieved by competitively binding to the antigen or by blocking the antibody's binding site, which can suppress the immune response against the antigen and thereby reduce the intensity of the immune reaction. Ab2 can also interact with T cells, suppressing inflammatory responses and autoimmune reactions.
Regarding immune activation, anti-idiotypic antibodies can act as immunogens, stimulating the body to produce an immune response against its own antibodies. This can promote the activation and proliferation of the immune system, as well as stimulate the proliferation and differentiation of B cells.
(2) Immune Network Theory
In 1974, based on modern immunology's understanding of antibody molecule idiotypes and building upon Burnet's "Clonal Selection Theory," Swedish immunologist Niels Jerne proposed the famous "Immune Network Theory" to explain the self-regulation of immune responses within the immune system.
According to this theory, the immune system is composed of interconnected different types of immune cells and molecules. Ab2 can act as one of the key molecules in this immune network, interacting with other immune cells and molecules to collectively maintain the body's immune balance.
IV. Application of Anti-Idiotypic Antibodies in Vaccines
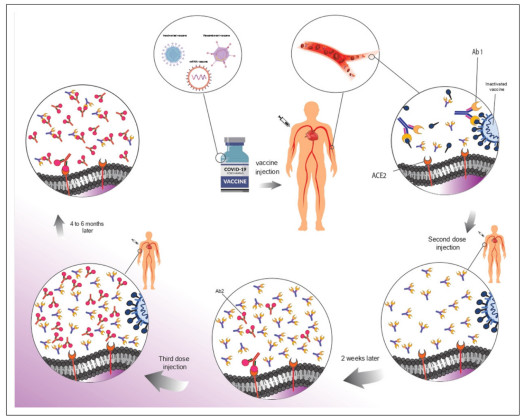
1. Study of Anti-Idiotypic Antibodies and Antinuclear Antibodies in Recipients of Three Doses of COVID-19 Vaccine
One factor potentially reducing vaccine efficacy is the anti-idiotypic network. Anti-idiotypic antibodies can bind to the somatic receptors that the antigen of the primary antibody binds to; this may lead to pathological complications, especially after a longer period.
A study investigated the presence of anti-idiotypic antibodies and ANAs in individuals who had received three doses of a COVID-19 vaccine, checking at least 4 months after the third dose. A double antibody sandwich ELISA was used to detect anti-RBD anti-idiotypic antibodies, antinuclear antibodies (ANAs), and SARS-CoV-2 anti-IgG RBD levels in the serum of 180 subjects.
In the anti-RBD anti-idiotypic antibody assay, 14 individuals (7.7%) had anti-idiotypic antibodies, while 166 (92.3%) did not. Five cases (2.7%) were ANA positive (>50 RU/mL), and 175 (97.3%) were ANA negative (<50 RU/mL). Examination of the quantitative results for SARS-CoV-2 anti-IgG RBD revealed that all 180 individuals (100%) enrolled in the study had anti-RBD antibody titers.
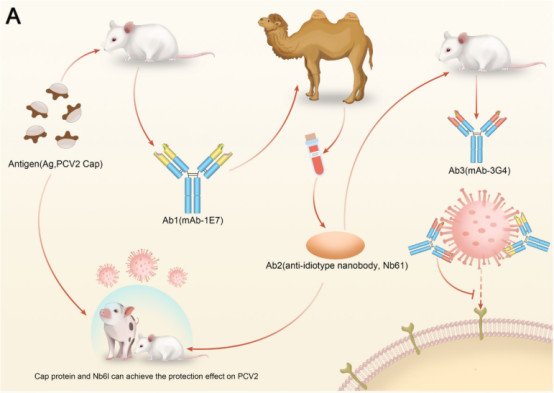
2. A Novel Anti-Idiotype Vaccine Strategy: Nanobodies Mimicking the Neutralizing Epitope of Porcine Circovirus Type 2
Vaccination is the most effective method to protect humans and animals from diseases. As they do not contain the pathogenic agent, anti-idiotypic vaccines are safer. However, the commercial production of traditional anti-idiotypic vaccines using monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies is complex and has a high failure rate.
Camels were immunized with a neutralizing monoclonal antibody (mAb-1E7, Ab1) targeting the PCV2 capsid protein (PCV2-Cap). Twelve nanobodies against mAb-1E7 were screened. Among them, NB61 (Ab2) targeted the idiotopic epitope of mAb-1E7 and blocked the binding of mAb-1E7 to PCV2-Cap. Furthermore, high-dose NB61 vaccination could also protect mice and pigs from PCV2 infection. Epitope mapping analysis indicated that mAb-1E7 recognizes the PCV2-Cap epitope containing the sequence 75NINDFL80, while NB61 contains the sequence 101NYNDFLG107. Subsequently, a monoclonal antibody (mAb-3G4, Ab3) against NB61 was produced, which could neutralize PCV2 infection in PK-15 cells. Structural analysis revealed that the amino acids of mAb-1E7 and mAb-3G4 involved in binding to PCV2-Cap and NB61, respectively, were also similar in amino acid sequence and spatial conformation.
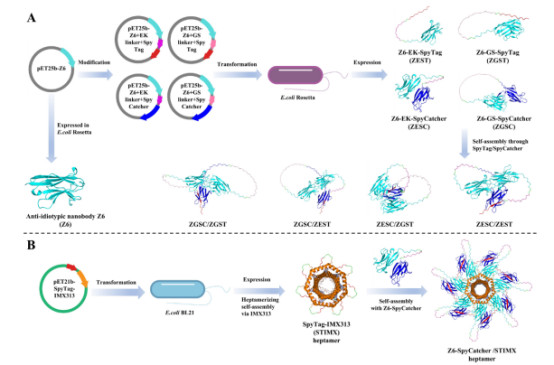
V. Application of Anti-Idiotypic Antibodies in Hapten Detection
Using zearalenone (ZEN) and deoxynivalenol (DON) as hapten models, a study achieved the in vitro self-assembly of bivalent and bispecific anti-idiotypic nanobodies by fusing them with SpyCatcher/SpyTag peptides. The results showed that the modified nanobodies had significantly improved sensitivity (e.g., the IC₅₀ for the DON anti-idiotypic nanobody decreased from 0.28 ng/mL to 0.18 ng/mL). Furthermore, the bispecific nanobodies could simultaneously recognize both mycotoxins, providing a new strategy for multi-target hapten detection.
VI. Anti-Idiotypic Antibody Development Services
Start Bio provides customized anti-idiotypic antibody development services, offering a complete package from antigen preparation and anti-idiotypic antibody development to the establishment of detection methods. The drug types involved include monoclonal antibody drugs, nanobody drugs, etc., and the ADA antibody types include neutralizing and non-neutralizing types. Start Bio offers multiple development plans tailored to customer needs, accelerating your antibody drug research and development endeavors.
VII. Case Studies of Custom Anti-Idiotypic Antibody Services
Case Study: Anti-Idiotypic Polyclonal Antibodies
Target: Monoclonal Antibody Drug
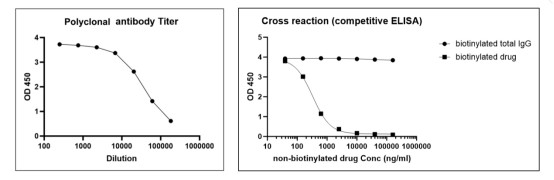
Deliverable: 20mg of specific anti-idiotypic polyclonal antibodies
Case Study: Anti-Idiotypic Monoclonal Antibodies
Target: Monoclonal Antibody Drug
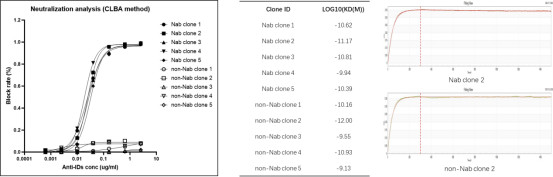
Deliverable: 5 neutralizing and 5 non-neutralizing monoclonal antibody clones
Related News
- Wnt3a Cytokine: A Multidimensional Exploration from Molecular Characteristics to 12/31/2026
- Tahoe Therapeutics generates the largest single-cell atlas ever using INTEGRA Bi 2/14/2026
- Evaluating the Clinical Value of Chromogranin A Antibodies in Neuroendocrine Tum 2/13/2026
- Unveiling the Multifaceted Value of CGA/HCG-α: From Pregnancy Monitoring to Dise 2/12/2026
- Azenta Life Sciences and Frontier Space Announce Strategic Partnership 2/12/2026
- Elucidating CD8α’s Core Mechanisms: Maintaining T Cell Homeostasis and Regulatin 2/11/2026
- GIC Invests US$100M in Ascletis Pharma (1672. HK): Anchoring Long-Term Capital i 2/11/2026
- AnalytiChem to Showcase New Product Launches and its Wide-ranging Lab Solutions 2/11/2026
- CD79B Antibodies: Emerging as a Precise Target for B Cell-Related Disease Therap 2/10/2026
- Everest Medicines Announces China NMPA Approval of VELSIPITY(R) for Adults with 2/10/2026


