Home > News > Ubiquitination Antibodies: How to Precisely Select the Appropriate Clone Based On Research Needs?
Ubiquitination Antibodies: How to Precisely Select the Appropriate Clone Based On Research Needs?
- Recent Advances
I. Molecular Mechanisms and Functional Diversity of Ubiquitination
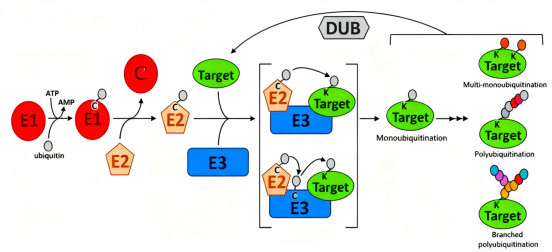
Ubiquitination, a highly conserved post-translational modification process in eukaryotic cells, involves a three-step enzymatic cascade comprising E1 activating enzymes, E2 conjugating enzymes, and E3 ligases. This process covalently attaches ubiquitin molecules (composed of 76 amino acids) to specific lysine residues on substrate proteins. This precise regulatory system can generate functionally diverse forms of ubiquitination, primarily determined by the structural characteristics of the ubiquitin chain.
K48-linked ubiquitin chains primarily mediate proteasomal degradation pathways, responsible for the selective degradation of intracellular proteins. K63 linkages participate in processes like DNA damage repair and inflammatory signaling. Linear ubiquitination, catalyzed by the linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex (LUBAC), plays a crucial role in the precise regulation of the NF-κB signaling pathway. This functional diversity necessitates targeted detection strategies for ubiquitination research.
II. Why Do Different Clone Antibodies Yield Differential Detection Results?
In ubiquitination research, antibodies with different clone numbers can exhibit distinctly different Western Blot banding patterns, primarily due to differences in epitope recognition characteristics. Antibodies recognizing "open" epitopes can bind to free ubiquitin, monoubiquitination modifications, and ubiquitin molecules within polyubiquitin chains. Therefore, in WB experiments, they produce continuous smeared bands, reflecting the complete distribution profile of ubiquitinated proteins in the sample.
In contrast, antibodies targeting "cryptic" epitopes can only recognize free ubiquitin and monoubiquitination modifications. When ubiquitin forms polyubiquitin chains, their recognition epitopes become buried within the chain and cannot be bound, resulting in discrete single or multiple specific bands in WB results. This difference in epitope selectivity directly determines the application scope of the antibody in specific research contexts.
III. How to Select Appropriate Ubiquitination Antibodies Based on Experimental Objectives?
When selecting ubiquitination antibodies, the primary consideration is the specific goal of the research. For analyzing global protein ubiquitination levels, priority should be given to antibodies capable of recognizing polyubiquitin chains. These antibodies typically produce characteristic smeared bands, comprehensively reflecting the overall changes in the ubiquitination state of the sample. Such antibodies are particularly suitable for assessing the effects of proteasome inhibitor treatment or monitoring abnormalities in protein degradation pathways.
When the research focus is on the dynamics of the free ubiquitin pool or when immunoprecipitation experiments are required, antibodies with high affinity for free ubiquitin are preferable. The discrete bands produced by these antibodies facilitate precise quantitative analysis and enable efficient capture of target molecules during immunoprecipitation. Furthermore, for studying specific types of ubiquitin chains, consideration should also be given to selecting linkage-specific antibodies.
IV. How Does Sample Type Influence Antibody Selection Decisions?
The characteristics of the experimental sample are an important reference factor in antibody selection. Whole cell lysates, especially those treated with proteasome inhibitors, contain abundant polyubiquitinated proteins and are most suitable for detection using smear-type antibodies. In contrast, cell models overexpressing free ubiquitin or purified ubiquitin protein samples are more suitable for analysis using band-type antibodies.
In complex biological samples, ubiquitination modifications exhibit high heterogeneity, including ubiquitin chains of different lengths and various linkage types. This complexity requires researchers to fully consider the abundance and distribution of the target ubiquitination forms in the sample during antibody selection to ensure detection sensitivity and specificity. If necessary, sample pre-treatment can be used to enrich specific types of ubiquitination modifications.
V. What Characteristics Should High-Quality Ubiquitination Antibodies Possess?
High-quality ubiquitination antibodies should possess several key characteristics:First is high specificity, capable of accurately distinguishing the target ubiquitination form without cross-reactivity;Second is good consistency between batches, ensuring the reliability and reproducibility of experimental results; third is extensive application validation, maintaining stable performance under various experimental conditions.
Furthermore, excellent products should also provide detailed technical documentation, including clear epitope localization information, applicable species cross-reactivity, and validated experimental condition recommendations. This information can help researchers quickly establish reliable experimental methods, avoiding waste of time and resources due to inappropriate antibody selection.
VI. How to Optimize Ubiquitination Detection Experimental Protocols?
Establishing a robust ubiquitination detection protocol requires systematic optimization of multiple steps. During the sample preparation stage, appropriate proteasome inhibitors and deubiquitinating enzyme inhibitors should be added to prevent alterations in ubiquitination modifications during the experimental process. Electrophoresis conditions should ensure effective separation of ubiquitinated proteins of different molecular weights, especially high molecular weight polyubiquitinated proteins.
The antibody incubation step requires optimization of working concentration and reaction time to ensure signal strength while minimizing non-specific binding. For result analysis, standard band interpretation criteria should be established to correctly distinguish specific signals from background noise. Only through systematic method optimization and strict quality control measures can the accuracy and reliability of ubiquitination research results be ensured.
VII. Which Companies Supply Ubiquitination Antibodies?
Hangzhou Start Biotech Co., Ltd. has independently developed the "Ubiquitin Recombinant Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody" (Product Name: Ubiquitin Recombinant Rabbit mAb (SDT-R095), Product Code: S0B0087). This is a protein post-translational modification detection antibody characterized by broad-spectrum recognition capability, high specificity, and excellent stability. Developed using recombinant rabbit monoclonal antibody technology, it efficiently recognizes both free ubiquitin and ubiquitination modifications on substrate proteins. It holds significant application value in protein ubiquitination identification, proteasome degradation pathway research, disease mechanism exploration, and targeted protein degradation drug development.
Core Product Advantages:
Broad-Spectrum Recognition Capability and High Specificity: Validated across multiple platforms including Immunoprecipitation, Western Blot, and Immunofluorescence, this product can recognize both monoubiquitination and polyubiquitination modifications, demonstrating exceptional broad-spectrum recognition characteristics. Its high specificity ensures accurate capture of ubiquitination signals within complex sample backgrounds, providing a reliable tool for functional research.
Excellent Stability and Batch Consistency: Under stringent production and quality control systems, the product exhibits outstanding physicochemical stability and minimal batch-to-batch variation, ensuring reliable and comparable results across different experimental batches, providing stable support for long-term research projects.
Suitable for Various Key Application Scenarios: This product is an ideal tool for the following research areas:
* Protein Ubiquitination Modification Identification: For detecting the level and pattern changes of ubiquitination modifications on specific proteins within cells.
* Proteasome Degradation Pathway Research: For studying the regulatory mechanisms of protein degradation via the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway.
* Neurodegenerative Disease Research: For exploring the association between abnormal protein aggregation and the ubiquitin system in diseases like Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease.
* Targeted Protein Degradation Drug Development: Serves as a key tool antibody for validating and assessing the efficacy of target protein degradation mediated by emerging technologies like PROTACs and molecular glues.
Professional Technical Support: We provide detailed product technical documentation, including validation data across various application platforms, experimental operation suggestions, and professional technical support, fully committed to assisting customers in achieving breakthroughs in the fields of protein function and drug development research.
For more details about the "Ubiquitin Recombinant Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody" (Product Code S0B0087) or to request a sample test, please feel free to contact us.
Product Information
| Catalog No. | Product Name | Product Parameters |
| S0F0018 | Premium Anti-K-ε-GG agarose Beads | |
| S0F0005 | Anti-K-ε-GG agarose Beads | |
| S0B0965 | K-ε-GG Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody | Host : Rabbit Conjugation : Unconjugated |
| S0B0087 | Ubiquitin Recombinant Rabbit mAb (SDT-R095) | Host : Rabbit |
Related News
- Wnt3a Cytokine: A Multidimensional Exploration from Molecular Characteristics to 12/31/2026
- Tahoe Therapeutics generates the largest single-cell atlas ever using INTEGRA Bi 2/14/2026
- Evaluating the Clinical Value of Chromogranin A Antibodies in Neuroendocrine Tum 2/13/2026
- Unveiling the Multifaceted Value of CGA/HCG-α: From Pregnancy Monitoring to Dise 2/12/2026
- Azenta Life Sciences and Frontier Space Announce Strategic Partnership 2/12/2026
- Elucidating CD8α’s Core Mechanisms: Maintaining T Cell Homeostasis and Regulatin 2/11/2026
- GIC Invests US$100M in Ascletis Pharma (1672. HK): Anchoring Long-Term Capital i 2/11/2026
- AnalytiChem to Showcase New Product Launches and its Wide-ranging Lab Solutions 2/11/2026
- CD79B Antibodies: Emerging as a Precise Target for B Cell-Related Disease Therap 2/10/2026
- Everest Medicines Announces China NMPA Approval of VELSIPITY(R) for Adults with 2/10/2026


