Home > News > Is There an Inevitable Link Between PD-1 Antibody Half-Life and Clinical Efficacy?
Is There an Inevitable Link Between PD-1 Antibody Half-Life and Clinical Efficacy?
- Recent Advances
I. Why Do Antibody-Based Drugs Have Unique Pharmacokinetic Characteristics?
The in vivo processes of protein-based drugs are fundamentally different from those of traditional small-molecule drugs. Due to the action of gastrointestinal proteases, biological macromolecules like monoclonal antibodies cannot be administered orally and are typically delivered directly into the circulatory system via intravenous or subcutaneous injection. Unlike small-molecule drugs, which distribute widely to various tissues and organs via passive diffusion, the tissue distribution of antibody drugs is significantly restricted by their large molecular size. Their primary distribution is limited to capillary beds with fenestrated structures, such as those in the kidneys, liver, and spleen.
Regarding metabolic pathways, antibody drugs are primarily internalized into cells via endocytosis and degraded into amino acids within lysosomes, with some metabolites potentially being reused by the body. This process is distinctly different from the metabolism of small-molecule drugs, which relies on the hepatic cytochrome P450 enzyme system. Particularly unique is that antibody drugs can be recycled through binding to the neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn). This mechanism effectively protects antibodies from lysosomal degradation, thereby significantly extending their plasma half-life.
II. How Does the Mechanism of Action of PD-1 Antibodies Influence Their Pharmacodynamic Characteristics?
PD-1 inhibitors work by specifically binding to the Programmed Death Receptor-1 on T cells, blocking its interaction with the ligands PD-L1/PD-L2, thereby relieving the suppression of T cell activation and enhancing the anti-tumor immune response. This unique mechanism of action fundamentally distinguishes the pharmacodynamic profile of PD-1 antibodies from traditional cytotoxic drugs.
Studies on key pharmacodynamic indicators show that PD-1 antibodies bind to their target with high affinity and slow dissociation kinetics. Clinical data confirm that PD-1 antibodies with different half-lives can all maintain greater than 70% target occupancy for several weeks after a single dose. This sustained high occupancy state is facilitated by the stability of the antibody-receptor complex, resulting in a non-linear relationship between plasma drug concentration and target occupancy. This characteristic is markedly different from the concentration-dependent effect model of traditional small-molecule drugs.
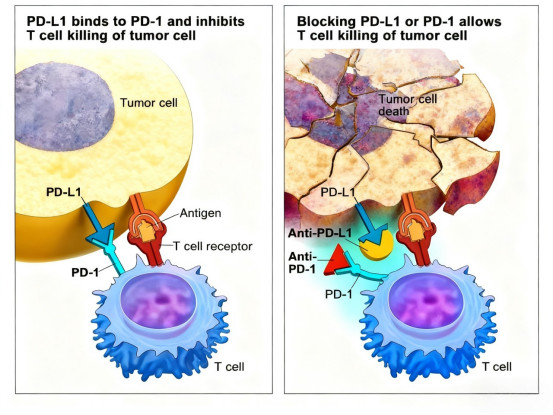
III. Do Half-Life Differences Determine the Clinical Efficacy of PD-1 Antibodies?
Currently approved PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors exhibit significant variation in their half-lives, ranging from several days to three weeks. According to traditional pharmacological theory, a shorter half-life might necessitate more frequent dosing to maintain effective blood concentrations. However, clinical study data show that PD-1 antibodies with different half-lives demonstrate comparable anti-tumor activity under the same dosing intervals.
This seemingly paradoxical phenomenon can be explained by the unique mechanism of action of PD-1 antibodies. Because the antibody forms a stable complex with its target after binding, its biological effect no longer depends solely on plasma drug concentration but is determined by the more direct pharmacodynamic indicator – target occupancy. Therefore, even PD-1 antibodies with shorter half-lives can maintain a sustained pharmacological effect as long as sufficient target occupancy is achieved early in treatment. This characteristic makes half-life less critical for predicting the efficacy of PD-1 inhibitors.
IV. What is the Relationship Between Half-Life and Immune-Related Adverse Events?
Immune-related adverse events (irAEs) associated with immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy are a significant clinical concern. Their mechanism of occurrence is closely related to the drug's mechanism of action: blocking the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway, while activating anti-tumor immunity, may also disrupt self-immunological tolerance, leading the immune system to attack normal tissues.
Some studies suggest that PD-1 antibodies with longer half-lives might be associated with a higher incidence of irAEs. Theoretically, the persistent presence of the drug could prolong the abnormal activation state of the immune system, increasing the risk of autoimmune reactions. Clinical observations indicate that drugs with half-lives exceeding 15-20 days that maintain high target occupancy might require closer monitoring for adverse reactions. However, this association still needs confirmation from more prospective studies, and the occurrence of irAEs is also influenced by various factors such as patient-specific factors and tumor type.
V. How to Optimize the Clinical Use Strategy of PD-1 Antibodies?
Based on the unique pharmacological characteristics of PD-1 antibodies, clinical dosing strategies should comprehensively consider multiple factors. Regarding efficacy, the focus should be on achieving and maintaining target occupancy, rather than solely pursuing plasma drug concentrations. For safety management, it is essential to establish comprehensive procedures for monitoring and managing irAEs, including timely recognition, grading management, and standardized use of immunosuppressants.
Notably, PD-1 antibodies with shorter half-lives might offer more flexibility for treatment adjustments, allowing for a quicker cessation of drug effect in case of severe adverse events. This characteristic is particularly important for patients requiring combination therapy or those with pre-existing autoimmune conditions. Furthermore, the development of dosing regimens must also consider patient convenience and healthcare resource utilization efficiency, optimizing the treatment experience while ensuring efficacy.
In summary, the relationship between the half-life characteristics of PD-1 antibodies and their clinical value is complex. Clinical decision-making should be based on a comprehensive judgment of the drug's pharmacodynamic characteristics, safety data, and individual patient factors, rather than relying solely on pharmacokinetic parameters. With a deeper understanding of the mechanisms of immune checkpoint inhibitors, more precise dosing strategies and individualized treatment plans are likely to emerge in the future.
VI. Which Manufacturers Provide PD-1 Antibodies?
Hangzhou Start Bio-tech Co., Ltd. (ANT BIO PTE. LTD. group member) 's self-developed "PD-1 Recombinant Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody" is a high-performance antibody product characterized by high specificity, excellent sensitivity, and exceptional staining consistency. This product is ideal for applications such as companion diagnostics for cancer immunotherapy, T cell function research, and immune microenvironment analysis.
Product Core Advantages:
* High Specificity & Clear Membrane Localization: Precisely recognizes the Programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) antigen, demonstrating excellent cell membrane-specific staining in both FFPE tissue sections and cell samples, with clear background and accurate localization, providing a reliable basis for precise interpretation.
* Excellent Staining Stability & Batch Consistency: Under strict quality control standards, the product exhibits excellent staining/labeling stability and minimal batch-to-batch variation, ensuring high comparability of results across different laboratories and experimental batches, providing stable support for clinical diagnostics and translational research.
* Suitable Key Application Scenarios:
This product is an ideal tool for conducting the following research:
Companion Diagnostics for Cancer Immunotherapy: For detecting PD-1 expression levels on Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes (TILs), providing reference for predicting the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors.
T Cell Exhaustion Status Assessment: For evaluating the degree of exhaustion and functional status of T cells in pathological states such as chronic infections and cancer.
Immune Microenvironment Research: For studying the distribution and function of PD-1+ immune cells in the tumor microenvironment, autoimmune diseases, and transplantation immunology.
Drug Development & Efficacy Prediction: Serves as a key tool antibody for exploring the mechanisms of action of immunotherapeutic drugs and developing biomarkers in preclinical research.
* Professional Technical Support: We provide detailed product technical documentation, including complete IHC and flow cytometry protocols, optimized experimental conditions, and professional interpretation guidance, fully committed to assisting customers in achieving accurate and reliable results in cancer immunotherapy research and clinical applications.
ANT BIO PTE. LTD. is always dedicated to providing high-quality, high-value biological reagents and solutions for global innovative pharmaceutical companies and research institutions. For more details about the "PD-1 Recombinant Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody" or to request a sample test, please feel free to contact us.
Product Information
| Catalog No. | Product Name | Product Parameters |
| UA010292 | PD-1 His Tag Protein, Mouse | Host : Mouse Expression System : HEK293 Conjugation : Unconjugated |
| UA010304 | PD-1 Fc Chimera Protein, Cynomolgus | Host : Cynomolgus Expression System : HEK293 Conjugation : Unconjugated |
| UA010301 | PD-1 mFc Chimera Protein, Mouse | Host : Mouse Expression System : HEK293 Conjugation : Unconjugated |
| S0B1811 | PD-1 Recombinant Rabbit mAb (Alexa Fluor® 555 Conjugate) (SDT-035-25) | Host : Rabbit Conjugation : Alexa Fluor® 555 |
| S0B2037 | PD-1 Recombinant Rabbit mAb (SDT-035-25) | Host : Rabbit Conjugation : Unconjugated |
Related News
- Wnt3a Cytokine: A Multidimensional Exploration from Molecular Characteristics to 12/31/2026
- Tahoe Therapeutics generates the largest single-cell atlas ever using INTEGRA Bi 2/14/2026
- Evaluating the Clinical Value of Chromogranin A Antibodies in Neuroendocrine Tum 2/13/2026
- Unveiling the Multifaceted Value of CGA/HCG-α: From Pregnancy Monitoring to Dise 2/12/2026
- Azenta Life Sciences and Frontier Space Announce Strategic Partnership 2/12/2026
- Elucidating CD8α’s Core Mechanisms: Maintaining T Cell Homeostasis and Regulatin 2/11/2026
- GIC Invests US$100M in Ascletis Pharma (1672. HK): Anchoring Long-Term Capital i 2/11/2026
- AnalytiChem to Showcase New Product Launches and its Wide-ranging Lab Solutions 2/11/2026
- CD79B Antibodies: Emerging as a Precise Target for B Cell-Related Disease Therap 2/10/2026
- Everest Medicines Announces China NMPA Approval of VELSIPITY(R) for Adults with 2/10/2026


